Virtual Reality (VR) headsets rely on display technologies to create immersive experiences. LCD and OLED are the two leading contenders in this space. This article dives deep into the pros and cons of each, examining their impact on image quality, performance, and overall VR immersion. Whether you're a VR enthusiast, a developer, or simply curious about the technology behind VR, this comprehensive comparison will provide valuable insights to help you understand which display technology is best suited for virtual reality.
Before diving into the specifics of how LCD and OLED displays perform in VR, it's essential to understand the fundamental differences between these two prevalent display technologies. Both are used in various applications, from smartphones to televisions, but their underlying mechanisms differ significantly.
A liquid crystal display (LCD) relies on a liquid crystal layer sandwiched between two glass substrates. These liquid crystal materials manipulate the polarization of light passing through them when an electric field is applied. A backlight, typically LED-based, provides the light source that illuminates the liquid crystals. By controlling the orientation of the liquid crystals for each pixel, an image is formed. The intensity and color of each pixel are determined by the amount of light that passes through the liquid crystal layer and color filters.
An organic light emitting diode (OLED) display, on the other hand, doesn't require a backlight. Each pixel in an OLED display is made up of organic compounds that emit light when an electric current is passed through them. This process is called electroluminescence. OLEDs offer individual pixel control, meaning each pixel can be turned on or off independently. This leads to superior contrast ratios, as true blacks can be achieved by simply turning off the corresponding pixels.
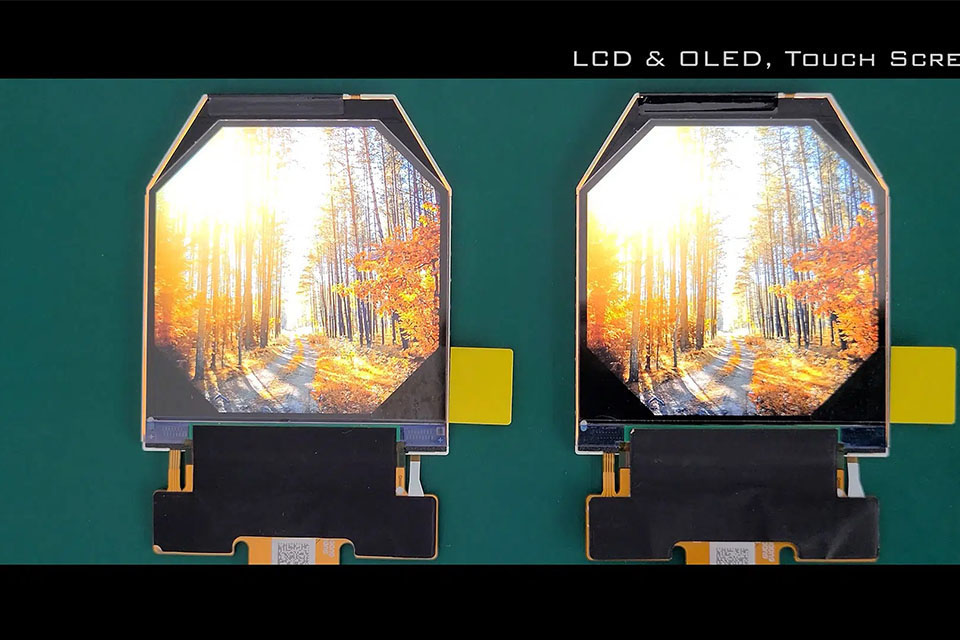

The display technology in a vr headset is arguably the most critical component affecting the overall experience. The image quality, refresh rate, and response time of the display directly influence the user's perception of reality within the virtual environment. Poor display performance can lead to motion sickness, eye strain, and a diminished sense of presence.
For virtual reality to feel truly immersive, the display must be capable of delivering high resolution, high refresh rates, and low persistence (the amount of time a pixel remains lit). High resolution ensures that the image appears sharp and detailed, minimizing the "screen door effect," where the individual pixels become visible. High refresh rates, typically 90Hz or higher, reduce motion blur and improve the fluidity of movement, leading to a more comfortable and responsive experience. Low persistence minimizes ghosting and blurriness when the user moves their head, further enhancing the sense of presence. The display panel is the window into the vr experience, and its capabilities define the limits of realism and comfort.
LCDs have been a popular choice for vr headsets, particularly in mainstream vr devices. This is largely due to their cost-effectiveness and technological maturity. LCD technology is well-established and widely available, making it a relatively affordable option for manufacturers.
While OLEDs are gaining traction, many early vr headsets and some current models still utilize lcd for vr. This is because lcd could achieve a decent balance between image quality, performance, and cost. However, it's important to note that not all lcds are created equal, and advancements in lcd technology, such as fast lcd panels and local dimming, have significantly improved their performance in vr applications.
LCDs offer several advantages that make them a viable option for vr displays. One of the most significant benefits is their high brightness. LCDs can achieve higher brightness levels compared to oleds, which can be advantageous in well-lit environments or for vr experiences that require vibrant colors. High brightness can enhance the perceived image clarity and make the virtual world feel more realistic.
Another advantage of lcds is their sharpness. Due to their subpixel arrangement and backlight system, LCDs can sometimes appear sharper than OLEDs at the same resolution. This can be particularly noticeable in text and fine details, making LCDs suitable for vr applications that involve reading or intricate visual elements. Moreover, lcds generally have longer lifespans compared to oleds, which are susceptible to burn-in (permanent image retention). Fast lcd technology has also helped address the issue of motion blur, making them more suitable for fast-paced vr experiences.
Here's a table summarizing the advantages and disadvantages of LCD technology in VR headsets:
| Feature | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Brightness | High brightness, good visibility in bright environments | Can appear washed out compared to OLEDs |
| Sharpness | Can appear sharper than OLEDs at the same resolution | Screen door effect can be noticeable |
| Cost | Generally more affordable than OLEDs | Contrast ratio limitations |
| Lifespan | Longer lifespan, less susceptible to burn-in | Motion blur can be an issue with traditional LCDs |
| Response Time | Fast LCD technology improves response time |
Despite their advantages, lcds also have some significant drawbacks that can impact the vr experience. The most prominent limitation is their contrast ratio. LCDs struggle to produce true blacks because the liquid crystal layer cannot completely block the backlight. This results in a lower contrast ratio compared to oleds, which can make the image appear washed out and less vibrant.
Another common complaint about lcds in vr is the "screen door effect." This occurs because the gaps between pixels are more visible on lcds compared to oleds, creating a noticeable grid-like pattern in the image. The screen door effect can detract from the immersion and make the virtual world feel less realistic. Furthermore, lcds typically have slower response times compared to oleds, which can lead to motion blur and ghosting, particularly in fast-paced vr experiences. This is something that fast lcd technology is trying to address to improve vr experience.

OLEDs have emerged as a strong contender in the vr display market, and they are often praised for their superior image quality and immersive capabilities. The key advantage of oleds is their ability to produce true blacks, which results in an incredibly high contrast ratio.
In an oled display, each pixel emits its own light, and when a pixel needs to display black, it is simply turned off. This results in perfect blacks and a stunning contrast ratio that is far superior to that of lcds. The high contrast ratio of oleds enhances the perceived depth and detail in vr experiences, making the virtual world feel more realistic and engaging. Oled display technology is known for its vibrant colors and excellent viewing angles. The wide color gamut and consistent color reproduction of oleds contribute to a more immersive and visually appealing vr experience.
The advantages of using oleds in vr headsets are numerous and significant. As mentioned earlier, the superior contrast ratio is a major selling point. The ability to display true blacks and vibrant colors creates a more realistic and immersive virtual world. Oled screens also offer faster response times compared to lcds, which minimizes motion blur and ghosting. This is crucial for creating a comfortable and responsive vr experience, especially in fast-paced games and simulations.
Oleds also offer wider viewing angles compared to lcds. This means that the image quality remains consistent even when the user's eyes are not perfectly aligned with the center of the display. This is particularly important in vr, where the user's head and eyes are constantly moving. Furthermore, oleds are more energy-efficient than lcds, especially when displaying dark scenes. This can lead to longer battery life in wireless vr headsets. The use of micro oled displays is allowing for even more compact form factor designs in next-generation vr devices.
Despite their numerous advantages, oleds also have some drawbacks that need to be considered. One of the main concerns is their high cost. Oled panels are generally more expensive to manufacture compared to lcd panels, which translates to a higher price for vr headsets that use oled displays. The high cost can be a barrier to entry for some consumers.
Another potential issue with oleds is burn-in. Over time, static images or elements that are displayed for extended periods can cause permanent image retention on the screen. While burn-in is less of a concern with modern oleds compared to earlier generations, it is still a factor to consider, particularly in vr applications where static elements such as heads-up displays (HUDs) are often present. Oleds also tend to have lower brightness compared to lcds. While this is not always a significant issue, it can be noticeable in well-lit environments or for vr experiences that require very high brightness levels. Furthermore, oleds can exhibit color shifting at extreme viewing angles, although this is less of a concern in vr headsets where the user's eyes are typically focused on the center of the display. Also, oleds have higher power consumption when displaying bright content, which can impact battery life in portable vr devices.
Here's a table summarizing the advantages and disadvantages of OLED technology in VR headsets:
| Feature | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Contrast Ratio | Superior contrast ratio, true blacks | Higher cost compared to LCDs |
| Response Time | Faster response time, minimal motion blur | Potential for burn-in with static elements |
| Viewing Angles | Wider viewing angles | Lower brightness compared to LCDs |
| Color | Vibrant colors, excellent color accuracy | Higher power consumption when displaying bright content |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower power consumption when displaying dark content |
Micro oled technology represents a promising direction for vr display development. Micro oled displays are manufactured directly onto silicon wafers, allowing for much higher pixel densities and smaller form factors compared to traditional oleds. This technology has the potential to address some of the limitations of both lcds and oleds in vr applications.
Micro oleds offer several key advantages. Their high pixel density can significantly reduce the screen door effect, resulting in a sharper and more immersive vr experience. The compact form factor allows for smaller and lighter vr headsets, which can improve comfort and reduce neck strain. Furthermore, micro oleds can achieve fast response times and high refresh rates, minimizing motion blur and enhancing the fluidity of movement. Sony is one of the leading companies developing micro oled technology for vr applications, and their micro oled displays have demonstrated impressive performance in terms of resolution, contrast, and response time.
The choice between lcd and oled for vr headsets ultimately depends on individual priorities and budget considerations. Both technologies have their strengths and weaknesses, and the best option will vary depending on the specific vr application and user preferences.
If cost is a primary concern, lcds offer a more affordable entry point into vr. While lcds may not offer the same level of image quality as oleds, advancements in lcd technology, such as fast lcd panels and local dimming, have significantly improved their performance in vr applications. LCDs are a good option for users who prioritize brightness and sharpness and are less sensitive to contrast ratio limitations. If image quality and immersion are paramount, oleds are generally the preferred choice. The superior contrast ratio, vibrant colors, and fast response times of oleds create a more realistic and engaging vr experience. OLEDs are ideal for users who demand the best possible visual fidelity and are willing to pay a premium for it. Micro oled technology represents the future of vr displays, offering the potential to combine the best aspects of both lcds and oleds into a single, high-performance display.
LCDs: More affordable, higher brightness, can appear sharper, longer lifespan.
OLEDs: Superior contrast ratio, true blacks, faster response times, wider viewing angles.
Screen Door Effect: More noticeable on LCDs due to pixel gaps.
Motion Blur: Less of an issue on OLEDs due to faster response times. Fast LCDs are trying to address this issue.
Contrast Ratio: OLEDs offer significantly higher contrast ratios than LCDs.
Burn-in: A potential concern with OLEDs, especially with static elements.
Power Consumption: OLEDs are more energy-efficient when displaying dark content, but less so with bright content.
Micro-OLED: Offers high pixel density and compact form factors, promising for future VR displays.
Virtual Reality: Display technology is crucial for creating an immersive and comfortable experience.
Best VR Display: The "best" display depends on individual priorities and budget.
Contact: Ashley Wu
Phone: +86 17773983073
E-mail: [email protected]
Add: 708 Room A Buiding Huafeng International Robot Industrial Park Xixiang Bao'an