This article dives deep into the transformative world of augmented reality (AR) displays, exploring the innovative technologies driving the next generation of AR solutions. We'll examine how these advancements are enhancing user experience, impacting various industries from automotive to gaming, and shaping the future of how we interact with information.
Why this article is worth reading:
Stay Ahead of the Curve: Gain insights into the latest developments in AR display technology.
Understand the Impact: Discover how AR displays are revolutionizing various sectors.
Explore Future Possibilities: Consider the potential applications and implications of next-generation AR.
Comprehensive Overview: Provides a detailed analysis of different AR display technologies.
Augmented reality (AR) is an interactive experience of a real-world environment where the objects that reside in the real world are enhanced by computer-generated perceptual information, sometimes across multiple sensory modalities, including visual, auditory, haptic, somatosensory and olfactory. In essence, AR seamlessly overlays digital content onto our view of the real-world, creating a mixed reality experience. Unlike virtual reality (VR), which completely immerses you in a virtual environment, augmented reality seeks to enhance your perception of the existing world. This enhancement is achieved through various technologies, but the display is paramount.
The ar display is the technology that makes this overlay possible. Think of it as a specialized screen that projects computer-generated images onto the user's field of view. This display can take many forms, from smartphone screens to ar glasses and headsets. The core function of an ar display is to integrate digital content with the real-world environment, allowing users to see and interact with both simultaneously. This can be anything from directions overlaid on a road while driving, to instructions appearing on a machine during maintenance.

While AR has already made significant strides, existing display technology often falls short of delivering a truly compelling and useful augmented reality experience. Early ar systems were often bulky, offered limited field of view, had poor image quality, and suffered from issues like aberration and low brightness. These limitations hindered the adoption of ar in wide range of applications. The need for next-generation ar display technology stems from the desire to overcome these limitations and enhance the user experience.
Next generation ar displays are focusing on creating display systems that are more compact, lightweight, and comfortable to wear. They strive to offer a wider field of view, allowing users to see more of the digital content within their real-world environment. Improved image quality, with higher resolution, brightness, and contrast, is also crucial for creating a more realistic and engaging augmented reality experience. Ultimately, the goal is to develop display technology that is so seamless and intuitive that users forget they are wearing ar glasses at all, allowing them to focus on the task at hand.
An augmented reality display is a complex system consisting of several crucial optical components that work together to create the augmented reality experience. These components are responsible for generating, manipulating, and projecting the images that are seamlessly overlaid onto the real-world view.
Here are the key components:
Microdisplays: These are tiny screens that generate the images that will be projected. Common microdisplays technologies include LCD (Liquid Crystal Display), LCOS (Liquid Crystal on Silicon), and OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode).
Light Source: The light source illuminates the microdisplays, providing the necessary brightness for the projecting images. LEDs (Light-Emitting Diodes) are commonly used as light sources due to their efficiency and compact size.
Optics: The optics are a crucial component that magnifies, shapes, and directs the light from the microdisplays to the human eye. This system of lens and mirrors corrects distortions (aberration), ensures proper focus, and expands the field of view.
Combiner: The combiner is responsible for combining the light from the microdisplays with the light from the real-world environment. This can be done using beam splitters or other optical elements that allow both the computer-generated images and the real-world view to be seen simultaneously.
Waveguides: These are thin, transparent elements that transmit the image from the microdisplay to the human eye via total internal reflection. Waveguides enable ar eyewear to be thinner and lighter than traditional ar headsets.
The display technology used in ar glasses and ar headsets is constantly evolving, with various approaches vying for dominance. Each display technology has its own strengths and weaknesses, making it suitable for different ar ar solutions and wide range of applications.
Here are some of the most prominent types of ar display technologies:
Optical See-Through Displays: These display systems use partially reflective mirrors or prisms to combine the computer-generated images with the user's view of the real-world. This allows the user to see both the real and virtual elements directly, without needing to look at a screen. Ar glasses often employ optical see-through display technology.
Video See-Through Displays: Video see-through displays use cameras to capture the real-world view, which is then displayed on a screen inside the headset. Computer-generated images are then overlaid onto the real-world video feed. This approach allows for greater control over the augmented reality experience and can offer advantages in terms of image quality and depth perception.
Waveguide Displays: Waveguide display technology uses a thin, transparent waveguide to transmit light from a microdisplay to the eye. The light is bounced back and forth within the waveguide using total internal reflection, before being coupled out to the eye using a grating or holographic element. This approach enables very compact and lightweight ar eyewear.
Retinal Projection Displays: These display systems project images directly onto the retina of the human eye using a low-power laser or LED. This approach can deliver very sharp and high-resolution images, but it can also be more complex and expensive than other display technologies.
| Display Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Optical See-Through | Direct view of real-world, less latency | Limited field of view, image quality can be affected by ambient light | Early AR glasses, basic overlays |
| Video See-Through | Greater control over image, better depth perception | Higher latency, can feel less natural | Industrial training, complex AR applications |
| Waveguide | Compact and lightweight, potential for large field of view | Complex manufacturing, image quality can be variable | Next-generation AR glasses, wearable AR devices |
| Retinal Projection | Sharp and high-resolution images, potentially wide field of view | Complex technology, potential safety concerns | Specialized applications, future AR headsets |
Optical performance is critical for delivering a convincing and enjoyable ar experience. The quality of the optics directly affects the clarity, sharpness, and stability of the augmented reality image, as well as the overall comfort and immersion for the wearer. Poor optical performance can lead to eye strain, headaches, and a diminished sense of presence.
Several key factors contribute to optical performance:
Resolution: High-resolution displays are essential for rendering sharp and detailed computer-generated images. A higher pixel density results in a more realistic and true-to-life visualization.
Field of View: A wider field of view allows users to see more of the digital content within their real-world environment, increasing the sense of immersion. A narrow field of view can feel restrictive and unnatural.
Brightness and Contrast: Sufficient brightness and contrast are necessary to ensure that the computer-generated images are visible in a variety of lighting conditions. Low brightness can make the ar experience difficult to see in bright sunlight.
Distortion and Aberration: Aberration and distortion can cause the augmented reality image to appear blurry, warped, or misaligned with the real-world environment. Optical system designers must carefully correct for these issues to ensure a clear and accurate visualization.
Developing advanced ar displays presents a multitude of technical challenges. Creating a display technology that is compact, lightweight, comfortable, high-resolution, and offers a wide field of view is no easy feat. Moreover, ar displays must also be energy-efficient and affordable to be commercially viable.
Here are some of the key challenges:
Optical Design: Designing optics that can deliver a clear, sharp, and distortion-free augmented reality image across a wide field of view is extremely challenging. Optical engineers must carefully balance competing requirements and correct for various aberration and distortions.
Microdisplay Technology: Microdisplays must be small, energy-efficient, and capable of producing high-resolution images with high brightness and contrast. Finding suitable microdisplays that meet these requirements can be difficult.
Waveguide Technology: Manufacturing waveguides with the necessary precision and uniformity is a significant challenge. Waveguides must be incredibly thin and transparent, with precisely controlled optical properties.
Computational Power: Ar display systems require significant computational power to process real-time data from sensors and cameras, render computer-generated images, and integrate the digital content with the real-world environment. This requires powerful and efficient processors and graphics cards.
Comfort and Social Acceptability: Ar headsets and ar glasses must be comfortable to wear for extended periods and socially acceptable in public. Bulky and heavy ar headsets can be uncomfortable and off-putting. Help reduce the eye crossing. Fixed focus distance is crucial to ensure social comfort.
Cost: The cost of ar display technology is a significant barrier to adoption. Ar headsets and ar glasses must be affordable to reach a mass market.
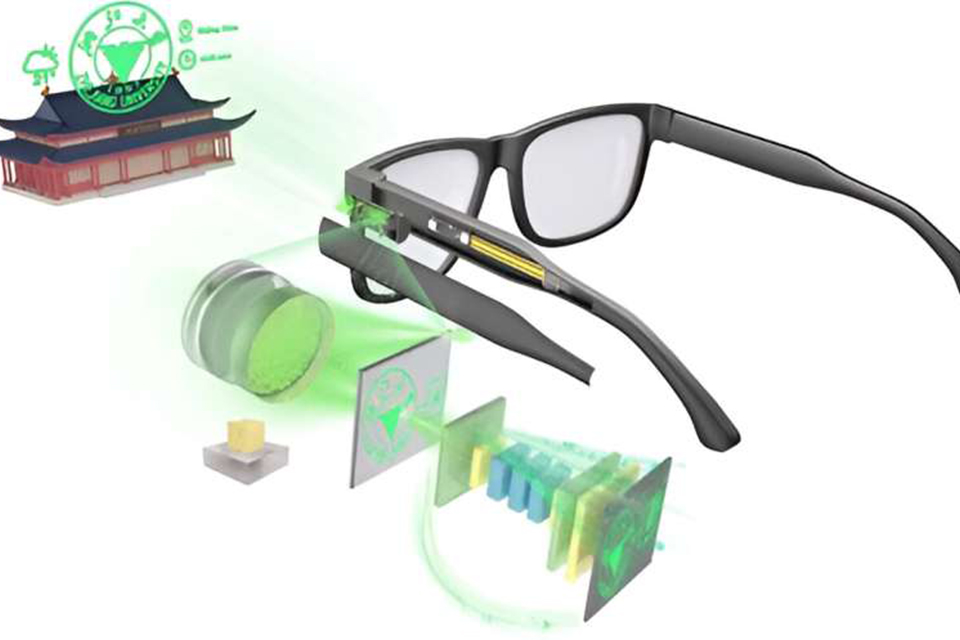
Ar displays are finding wide range of applications across various industries, transforming the way we work, learn, and interact with the world around us. From automotive to healthcare to gaming, ar display technology is revolutionizing processes and creating new possibilities.
Here are some of the most prominent current applications:
Automotive: Ar displays are being integrated into automotive hud to provide drivers with real-time information about their surroundings, such as navigation directions, speed limits, and hazard warnings. This helps to improve safety and enhance the driving experience.
Manufacturing: Ar display systems are used in manufacturing to provide workers with step-by-step instructions, quality control checklists, and remote expert assistance. This can enhance efficiency, reduce errors, and improve safety.
Healthcare: Ar headsets are used in healthcare for surgical training, medical visualization, and patient education. Ar can help surgeons to plan and execute complex procedures, allowing medical professionals to visualization anatomical structures in 3D, and deliver information directly to patients.
Gaming and Entertainment: Ar displays are used in gaming and entertainment to create immersive and interactive experiences. Ar games can overlay digital content onto the real-world environment, allowing players to interact with virtual characters and objects in their own homes.
Retail: Ar display technology are used in retail to allow customers to virtually try on clothes, visualize furniture in their homes, and access product information. This can enhance the shopping experience and drive sales.
The automotive industry is rapidly adopting ar display technology to enhance driver safety and user experience. Ar hud project information onto the windshield of the car, allowing drivers to see real-time data without taking their eyes off the road. Ar display goes a step further by overlaying computer-generated images onto the real-world view, creating a more intuitive and informative driving experience.
Here are some examples of how ar displays are being integrated into automotive hud:
Navigation Guidance: Ar hud can project turn-by-turn directions onto the road ahead, making it easier for drivers to follow their route.
Hazard Warnings: Ar display technology can highlight potential hazards, such as pedestrians, cyclists, and other vehicles, help reduce the risk of accidents.
Lane Departure Warnings: Ar ar solutions can alert drivers if they are drifting out of their lane, helping to prevent accidents caused by driver fatigue or inattention.
Adaptive Cruise Control: Ar displays can show drivers the distance to the vehicle ahead and the set speed of the cruise control system.
By delivers data information onto the windshield, ar hud can enhance driver awareness and reduce distractions, making driving safer and more enjoyable.
The future of augmented reality display technology is bright, with ongoing research and development pushing the boundaries of what's possible. Next generation of ar display technology promises to be more compact, lightweight, and powerful than ever before, enabling a wider range of ar reality experience.
Here are some of the key trends shaping the future of ar display technology:
Miniaturization: Ar headsets and ar glasses are becoming increasingly smaller and more discreet. Next generation display systems will be even more compact, allowing ar eyewear to resemble regular glasses.
Improved Image Quality: Ar display technology are constantly improving image quality, with higher resolution, brightness, and contrast. This will lead to more realistic and immersive ar experiences.
Wider Field of View: Next generation ar displays will offer a wider field of view, allowing users to see more of the digital content within their real-world environment. This will increase the sense of immersion and presence.
Integration with Artificial Intelligence: Artificial intelligence will play a key role in future ar display systems, enabling more intelligent and context-aware augmented reality experiences.
New Display Technologies: New display technologies, such as microled, are emerging that promise to enhance the performance and capabilities of ar display systems.
The prnewswire recently reported on the collaboration between EPFL and CERN, where researchers are working on new optical components to enhance ar reality experience. With advancements in display technology, artificial intelligence, and other related fields, ar has the potential to transform the way we live, work, and interact with the world around us. Ar promises to seamlessly blend the physical world world with virtual to transform our lives.
Staying informed about the latest advancements in ar display technology is crucial for anyone interested in this rapidly evolving field. Numerous sources to support can provide valuable insights into the latest research and development, emerging trends, and practical applications of ar ar solutions.
Here are some resources to explore:
Industry Publications: Websites and magazines dedicated to display technology, ar, and vr often feature articles and reports on the latest advancements in ar display technology.
Conferences and Trade Shows: Attending industry conferences and trade shows, such as Display Week and AWE (Augmented World Expo), is a great way to see the latest ar display technology in action and network with industry experts.
Research Papers and Journals: Academic journals and research papers provide in-depth information on the underlying science and technology behind ar display systems.
Company Websites: Many companies that are developing ar display technology have websites that provide information about their products and services. Please visit these websites to learn more about their ar ar platforms.
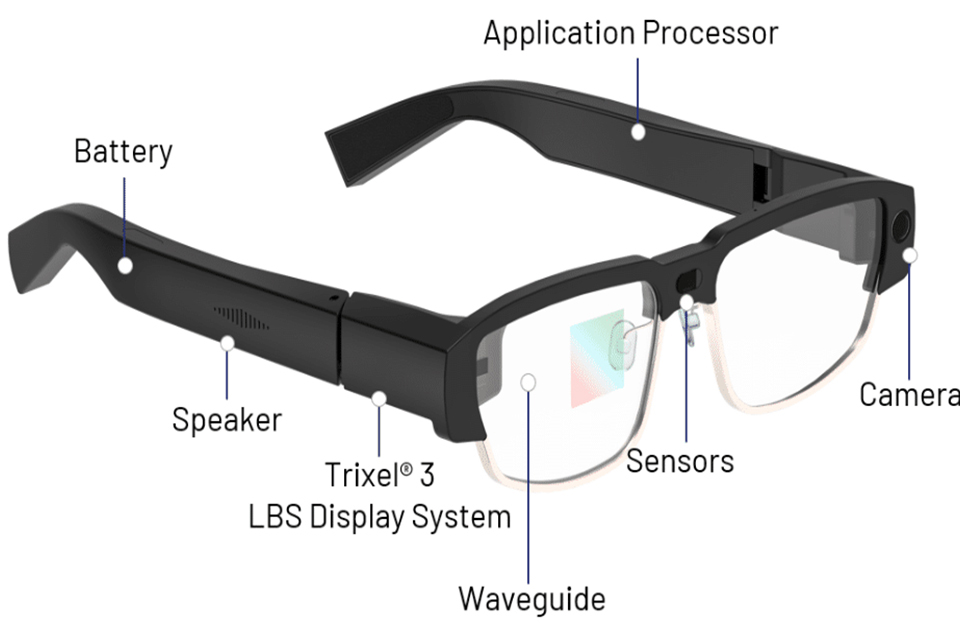
AR enhances reality: It overlays digital content onto the real-world, not replacing it like virtual reality (VR).
Displays are crucial: The display technology dictates the quality and usability of the ar experience.
Next-generation aims for seamlessness: The goal is to create ar eyewear that is comfortable, unobtrusive, and offers a wide field of view.
Various display technologies exist: From optical see-through to waveguides and retinal projection, each has its advantages and disadvantages.
Optical performance matters: Resolution, field of view, and distortion control are critical for a good ar experience.
Challenges remain: Miniaturization, optical design, and computational power are ongoing hurdles.
Applications are diverse: Ar is transforming industries from automotive to healthcare.
HUDs enhance driving: Ar hud project crucial information onto the windshield, improving safety and enhancement.
The future is bright: Expect smaller, more powerful, and more intelligent ar display technology.
Stay informed: Continuously learn about the latest ar display technology advancements through industry publications, conferences, and research and development.
Contact: Ashley Wu
Phone: +86 17773983073
E-mail: [email protected]
Add: 708 Room A Buiding Huafeng International Robot Industrial Park Xixiang Bao'an