Augmented Reality (AR) is transforming the way we interact with the world, seamlessly merging digital content with our physical surroundings. This article explores the common types of AR, providing insights into their functionalities, applications, and the technology behind them. Whether you are a tech enthusiast, a developer, or simply curious about AR, this informative guide will enhance your understanding of this fascinating field.
What is Augmented Reality?
What Are the Different Types of AR?
What is Marker-Based Augmented Reality?
What is Markerless Augmented Reality?
How Does Location-Based Augmented Reality Work?
What Are the Applications of Mobile Augmented Reality?
What is Projection-Based Augmented Reality?
What Are the Advantages of Different Types of AR?
How is AR Technology Evolving?
What Should You Remember About the Types of AR?
Augmented Reality (AR) is a technology that overlays digital information—such as images, sounds, and other sensory enhancements—onto the real world. Unlike Virtual Reality (VR), which creates an entirely immersive environment, AR enhances real-life experiences, allowing users to interact with both digital and physical elements simultaneously. This hybrid interaction opens up new possibilities for education, entertainment, and business.
AR is worth exploring because it is reshaping industries, from gaming and education to healthcare and retail. As AR technology continues to evolve, understanding its various types can help individuals and businesses leverage its capabilities effectively.

There are several types of AR, each with unique characteristics and use cases. Understanding these types is crucial for identifying how AR can be applied in different scenarios. The most common types include:
Marker-Based AR: Utilizes predefined images or patterns (markers) to trigger the display of digital content.
Markerless AR: Does not rely on markers; instead, it uses GPS, accelerometers, and digital compass data to overlay digital content.
Location-Based AR: Combines GPS data with AR to provide location-specific information.
Projection-Based AR: Projects digital information onto physical surfaces, allowing for interaction without the need for screens.
Mobile AR: Refers to AR experiences accessed through smartphones and tablets, enabling users to engage with AR content on the go.
By exploring these types further, we can gain insights into their functionalities and applications.
Marker-based AR uses physical markers—often QR codes or specific images—to trigger digital overlays. When the device's camera recognizes a marker, it superimposes a virtual object onto it. This type of AR is widely used in advertising and educational tools, providing interactive experiences that enhance user engagement.
For example, a marketing campaign may use a poster with a specific image as a marker. When a user scans this poster with an AR app, a 3D model or animation related to the product appears, providing additional information and an engaging experience.
Markerless AR, also known as location-based AR, relies on the device's sensors—such as GPS and accelerometers—to determine the user's location and orientation. This technology allows for a more flexible user experience since it does not depend on specific markers to display content.
For instance, a markerless AR application might allow users to see how a piece of furniture would look in their living room by using their smartphone camera to visualize the item in the actual space. This type of AR is particularly useful in retail, real estate, and gaming.
Location-based AR leverages GPS data to provide contextual information related to the user's geographical location. This type of AR is commonly used in applications such as tourism, where users can point their devices at landmarks to receive historical context, directions, or additional information.
For example, a location-based AR app might allow users to explore a city by pointing their phones at buildings. Digital overlays can display facts about the architecture or even highlight nearby attractions, enriching the user's experience of the physical environment.
Mobile AR is one of the most accessible forms of augmented reality, as it can be used on smartphones and tablets. This type of AR opens up a multitude of applications across different sectors, including:
Gaming: Popular games like Pokémon GO use mobile AR to create immersive experiences that encourage physical exploration.
Education: AR can facilitate interactive learning experiences, such as anatomy visualizations in medical education or historical reconstructions in classrooms.
Retail: Many brands utilize mobile AR to allow customers to virtually try on products, enhancing the shopping experience.
By integrating AR into mobile devices, businesses can engage consumers in innovative ways, leading to increased sales and customer satisfaction.
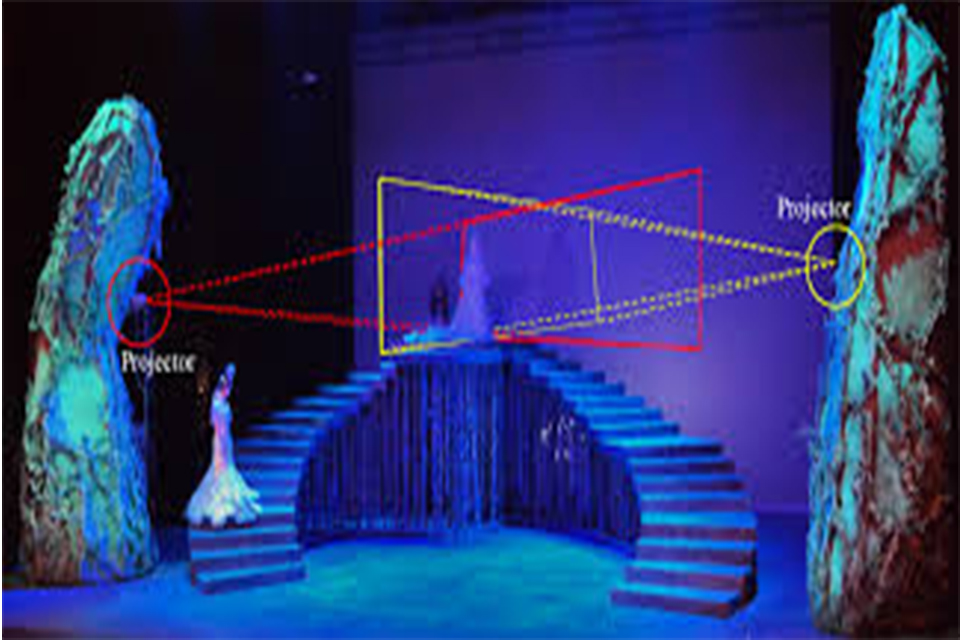
Projection-based AR projects digital images onto physical surfaces, enabling interaction without the need for handheld devices. This technology is often seen in exhibitions, art installations, and public displays.
For instance, in a museum, projection-based AR might be used to create interactive displays that tell the story of an artifact. Visitors can engage with the projected content, enhancing their understanding of the exhibit.
Each type of AR offers unique advantages, catering to various needs and preferences. Here are some benefits:
Marker-Based AR: Easy to implement and can provide high-quality visualizations when markers are correctly identified.
Markerless AR: Offers greater flexibility and usability, allowing users to interact with their environment seamlessly.
Location-Based AR: Provides contextually relevant information, making it ideal for navigation, tourism, and educational applications.
Projection-Based AR: Encourages group interaction and collaboration, as multiple users can see and engage with the same projected content.
Understanding these advantages can help businesses and developers choose the right type of AR for their specific use cases.
AR technology is rapidly advancing, with ongoing research and development leading to more sophisticated applications. Innovations in hardware and software are making AR experiences more immersive and accessible.
Key trends include the development of lightweight AR glasses, improvements in mobile processing power, and enhanced computer vision algorithms. These advancements aim to create seamless and intuitive AR experiences that integrate more naturally into everyday life.
Diverse Applications: AR technology is versatile, applicable in gaming, education, retail, and more.
User Experience: Different types of AR cater to varied user needs, enhancing interactivity and engagement.
Continuous Innovation: AR technology is evolving, promising more immersive and integrated experiences in the future.

Augmented Reality enhances the real world with digital information.
There are various types of AR: marker-based, markerless, location-based, and projection-based.
Each type has unique applications and advantages.
Mobile AR is widely accessible and impactful in multiple sectors.
Continuous advancements in AR technology are expanding its potential.
By understanding the different types of augmented reality, you can better appreciate how this technology shapes our interactions with the world and opens up new possibilities for the future.
Contact: Ashley Wu
Phone: +86 17773983073
E-mail: [email protected]
Add: 708 Room A Buiding Huafeng International Robot Industrial Park Xixiang Bao'an