Augmented reality (AR) has emerged as one of the most transformative technologies of the 21st century. But what exactly makes AR so groundbreaking? This blog dives deep into the key technologies powering AR, exploring how they shape immersive experiences and revolutionize industries. Whether you're a tech enthusiast, a professional, or just curious about AR, this article will give you valuable insights into how it works, where it's used, and where it's headed.
1. What is Augmented Reality (AR)?
Definition of AR and how it differs from VR and Mixed Reality (MR).
Why AR is becoming a cornerstone of modern technology.
2. Understanding the Core Technologies Behind AR
Overview of hardware and software components.
The role of 3D modeling and tracking in AR applications.
3. How Augmented Reality Works: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
Explanation of AR frameworks and algorithms.
The integration of sensors and cameras in AR devices.
4. Augmented Reality vs. Virtual Reality: What's the Difference?
Key distinctions between AR and VR.
Use cases where one technology outshines the other.
5. Examples of Augmented Reality in Everyday Life
Real-world applications like mobile AR and AR in gaming.
How AR is reshaping education, healthcare, and retail.
6. Augmented Reality in Manufacturing and Industry
How AR improves efficiency and safety in manufacturing.
Use cases in design, training, and remote assistance.
7. Key Technologies in AR: A Closer Look
SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping): Mapping the environment in real-time.
Advances in AR cloud technology for multi-user experiences.
8. The Future of Augmented Reality: What’s Next?
Emerging trends like extended reality (XR) and AI integration.
Predictions for AR’s impact on industries and society.
9. How AR Enhances Everyday Experiences
Personalized AR experiences in marketing and entertainment.
The role of AR in creating immersive 3D environments.
10. Integrating AR with Other Technologies
Exploring AR and VR combinations in hybrid systems.
How AR works alongside AI, IoT, and 5G for next-gen solutions.
Augmented reality (AR) overlays digital elements onto the real world, enhancing how we interact with our surroundings. Unlike virtual reality (VR), which immerses users in a fully digital environment, AR blends virtual objects with real-world settings.
For instance, AR applications like Pokémon GO use your smartphone's camera to bring virtual characters into the real world, offering an engaging and interactive experience.

AR technology combines hardware and software to create seamless digital overlays:
Hardware Components: Devices like AR glasses, headsets, and smartphones serve as platforms for AR experiences. Sensors and cameras capture real-world data, enabling AR to map environments accurately.
Software Tools: AR frameworks such as ARKit (Apple) and ARCore (Google) provide developers with tools to build robust AR applications. These frameworks handle tasks like object recognition and motion tracking.
AR experiences rely on three key processes:
Detection: Sensors and cameras scan the environment.
Processing: Software algorithms analyze the captured data, determining where and how to place digital objects.
Rendering: The AR system overlays 3D elements onto the real world, creating a unified visual experience.
For example, SLAM technology allows AR devices to map and track surroundings in real-time, essential for immersive experiences.
While both AR and VR are immersive technologies, they serve different purposes:
| Feature | Augmented Reality (AR) | Virtual Reality (VR) |
|---|---|---|
| Environment | Enhances the real world | Fully digital environment |
| Devices | Smartphones, AR glasses | VR headsets |
| Primary Use Cases | Navigation, training, retail | Gaming, simulations |
AR has found its way into various aspects of life:
Retail: Try-before-you-buy apps like IKEA Place let users visualize furniture in their homes.
Healthcare: AR-assisted surgeries improve precision and patient outcomes.
Education: AR apps turn learning into an engaging, interactive experience.
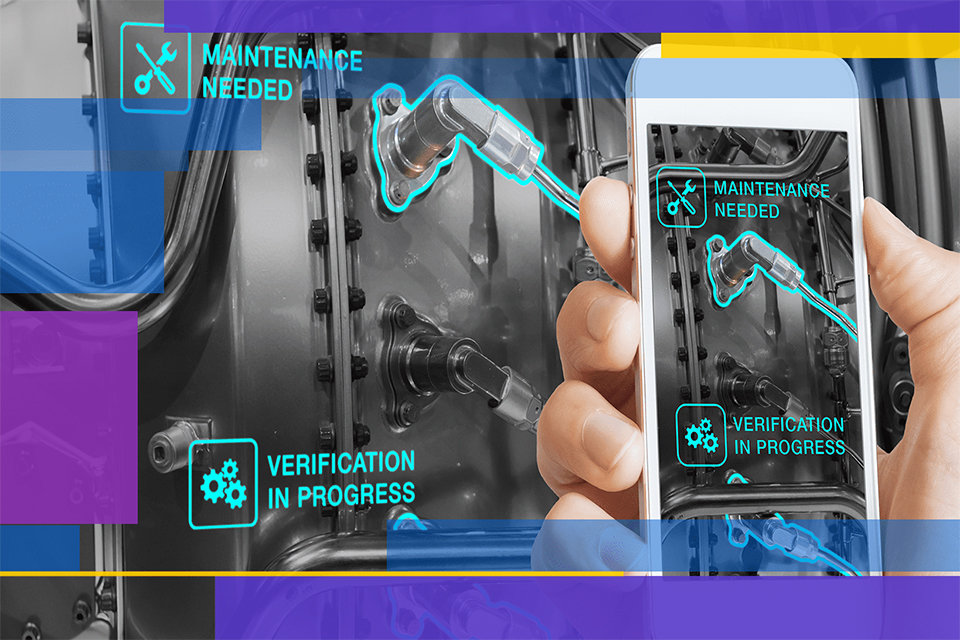
AR is revolutionizing manufacturing by enhancing productivity and safety:
Training Simulations: Workers use AR to learn complex tasks in a risk-free environment.
Remote Support: AR enables real-time guidance for troubleshooting machinery.
Design Prototyping: AR visualizes designs, reducing the need for physical prototypes.
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) is a critical component of AR. It ensures that virtual objects remain stable and accurately placed within the user’s field of view.
The AR cloud allows multiple users to interact with the same AR content in real-time, paving the way for collaborative AR applications.
The future of AR looks promising with advancements in extended reality (XR) and AI integration.
Extended Reality (XR): A convergence of AR, VR, and MR, enabling more immersive experiences.
AI in AR: AI improves AR by enabling object recognition, predictive analytics, and adaptive interfaces.

From interactive marketing campaigns to immersive games, AR adds value to both personal and professional experiences.
Marketing: AR lets brands engage with consumers through interactive ads and product demonstrations.
Entertainment: AR-powered games and apps captivate audiences with lifelike virtual interactions.
AR thrives when combined with other innovations:
IoT Integration: AR can visualize IoT data, providing real-time insights.
5G Networks: Faster connectivity enables smoother AR experiences.
AI and Machine Learning: Enhances personalization and efficiency in AR applications.
AR enhances reality by blending digital and physical worlds.
Core technologies like SLAM and AR cloud are pivotal to its success.
AR is transforming industries from healthcare to manufacturing.
The future of AR lies in its integration with AI, IoT, and 5G.
AR is not just a trend; it's a revolutionary tool reshaping how we interact with technology.
Explore the world of AR and witness the seamless convergence of technology and reality!
Contact: Ashley Wu
Phone: +86 17773983073
E-mail: [email protected]
Add: 708 Room A Buiding Huafeng International Robot Industrial Park Xixiang Bao'an