Augmented Reality (AR) glasses are rapidly changing how we interact with the world, merging digital information with our physical environment. This article dives deep into the fascinating technology behind AR glasses, exploring their core components, how they function, and their diverse applications. Reading this will equip you with a comprehensive understanding of AR glasses, from their fundamental principles to their exciting potential across various industries, enabling you to navigate the evolving landscape of augmented reality and understand the difference between ar and vr.
AR glasses are a type of wearable technology that overlay computer-generated images onto the user's view of the real world. Unlike virtual reality (VR) headsets, which create a completely virtual world, augmented reality (AR) enhances the physical world by superimpose digital content, such as text, images, and videos. This ar technology is a blend of the actual world and a digital one.
The fundamental difference lies in the level of immersion. VR aims to transport you to a different reality, blocking out the real environment entirely. AR glasses, on the other hand, keep you grounded in your surroundings, providing additional digital information and context without completely replacing your view. Imagine seeing directions overlaid on the street as you walk, or viewing information about a product as you look at it in a store – that's the power of ar.
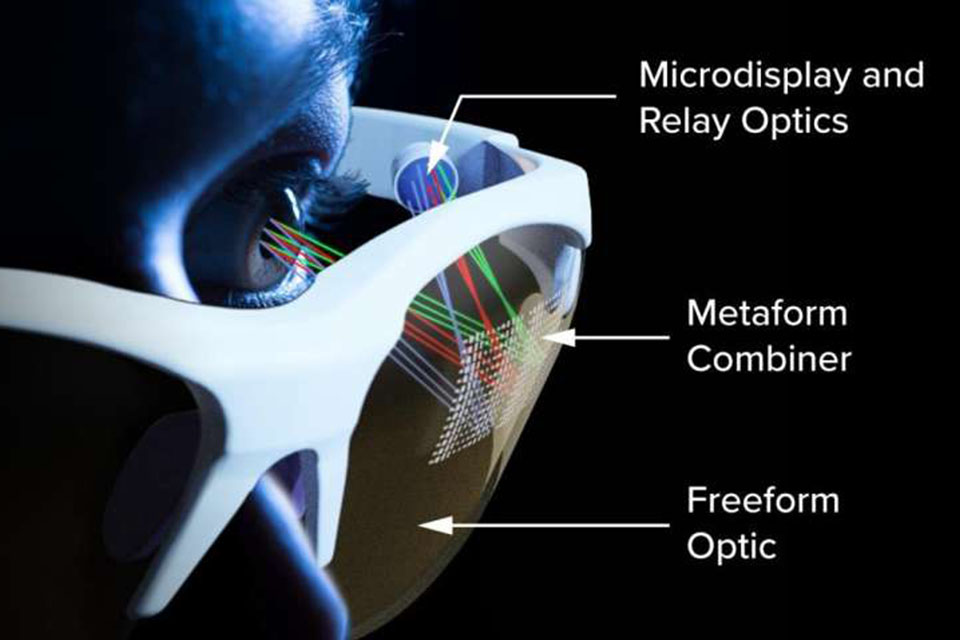
The magic behind how ar glasses work lies in their ability to seamlessly blend the digital and physical world. This is achieved through a complex interplay of hardware and software. First, sensors to track the user's head position and eye movements, allowing the ar system to understand precisely what the user is looking at. This data is then fed into a processor that renders the appropriate augmented reality content.
The rendered content is then projected onto the user's field of view using various optics technologies, such as waveguide or reflective displays. The goal is to make the digital information appear as if it's naturally part of the real environment, allowing the user to interact with it intuitively. The effectiveness of ar glasses use depends on how well this integration is achieved, ensuring the overlay doesn't feel artificial or distracting. The ar software is a very important part of the system.
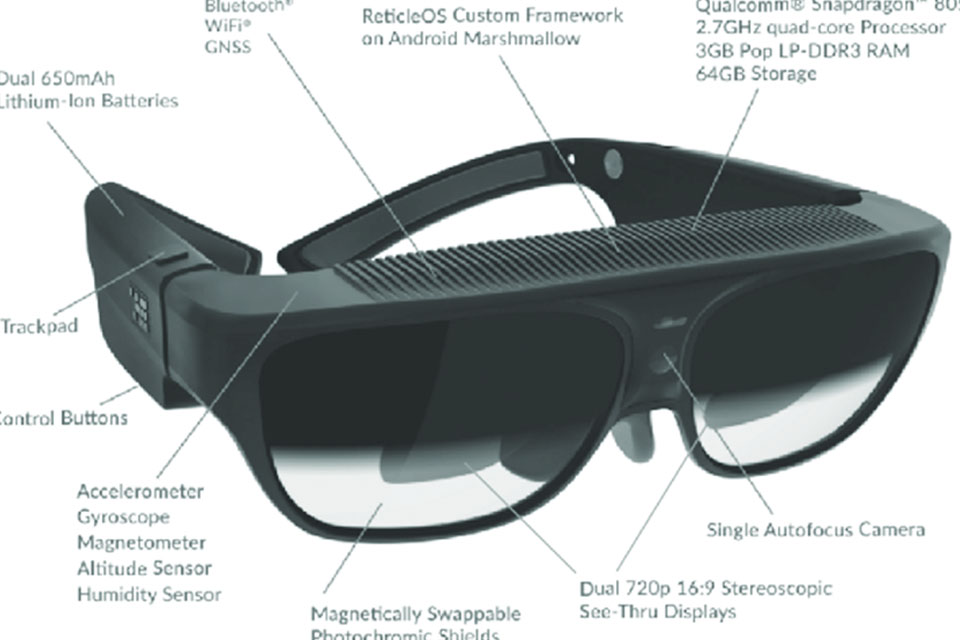
A pair of smart glasses isn't just a miniaturized computer strapped to your face; it's a carefully engineered system comprised of several glasses components working in harmony. Understanding these core components is crucial to appreciating how augmented reality is brought to life.
Display: Projects the digital information in front of your eyes.
Processor: The brains of the operation, responsible for processing data and rendering augmented reality content in real-time.
Sensors: Track your movement and surroundings, allowing the ar system to understand your context and adjust the display accordingly.
Camera: Captures the real environment, allowing the ar glasses to understand what you're looking at and overlay relevant information.
Battery: Powers the entire system, determining how long you can use of ar the ar glasses before needing to recharge.
Connectivity: Enables communication with other devices and the internet, allowing you to access data and collaborate with others.
These glasses components need to be compact, lightweight, and energy-efficient to create a comfortable and wearable experience. The typical ar glasses include all of these components.
The optics and display technology are at the heart of how ar smart glasses function, directly influencing the image quality and field of view. This is a critical component for any ar system. Several approaches are used to project images onto the user's eyes, each with its own set of advantages and challenges.
Waveguides: These use a thin, transparent piece of glass or plastic to guide light from a micro-display to the user's eye. Waveguides offer a wide field of view and can be made very thin, making them ideal for sleek smart glasses.
Reflective Displays: These use a series of mirrors to reflect the image from a micro-display into the user's eye. Reflective displays can offer high brightness and contrast but tend to be bulkier than waveguides.
Projectors: Some ar glasses use miniature projectors to beam images directly onto the user's retina. This approach can offer a very wide field of view and high image quality, but it can also be more complex and expensive.
The goal is to create a display that is bright, clear, and has a wide field of view so the ar content seamlessly blends onto the real world. Glasses must have a good display.
Sensors are the unsung heroes of ar glasses, playing a crucial role in understanding the user's environment and ensuring the augmented reality experience is accurate and responsive. These glasses include sensors that track a variety of parameters:
Position Tracking: Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs), including accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers, track the head movements and orientation of the ar glasses, allowing the system to understand where the user is looking.
Depth Sensing: Cameras or infrared sensors capture depth information about the environment, enabling the ar glasses to understand the distance to objects and construct a virtual map. This virtual map of the environment allows ar smart glasses to accurately place virtual objects in the real environment.
Eye Tracking: Some ar glasses incorporate eye-tracking technology to determine exactly where the user is looking. This information can be used to create a more natural and immersive experience, allowing the ar glasses to respond to the user's gaze.
The data from the sensors is processed in real-time to update the augmented reality display, ensuring the digital information remains accurately aligned with the real world.

AR glasses are rapidly expanding beyond consumer applications, finding practical glasses use across a diverse range of industries. Their ability to provide hands-free access to information and enhance collaboration makes them invaluable in various settings. The use of ar is growing more and more.
| Industry | Application | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Digital work instructions, remote expert assistance, quality control. | Increased efficiency, reduced errors, improved training, faster problem resolution. |
| Healthcare | Surgical guidance, medical training, patient education, remote consultations. | Enhanced precision, improved learning outcomes, better patient understanding, increased access to specialists. |
| Logistics | Warehouse navigation, order picking, inventory management. | Faster order fulfillment, reduced errors, improved efficiency, optimized workflows. |
| Field Service | Remote repair and maintenance, equipment diagnostics, on-site support. | Faster response times, reduced downtime, improved first-time fix rates, enhanced customer satisfaction. |
| Education | AR in learning: interactive learning experiences, augmented textbooks, virtual field trips. | Increased engagement, improved understanding, enhanced retention, access to immersive learning environments. |
| Retail | Interactive product displays, virtual try-on experiences, personalized shopping recommendations. | Increased sales, improved customer engagement, enhanced brand loyalty, personalized shopping experiences. |
| Architecture | Visualization of designs in the real-world, collaboration between architects and clients on-site. | Better understanding of designs, improved communication, faster decision-making, reduced design flaws. |
| Ar Remote Collaboration | Ar enables remote experts to see what on-site workers see and provide guidance in real-time. | Reduced travel costs, faster problem resolution, improved training, increased access to expertise. |
These are just a few examples of the many ways that ar glasses may be used to improve efficiency, enhance productivity, and provide new and innovative solutions across various industries.
AR glasses are poised to revolutionize the gaming and entertainment industries by creating truly immersive experiences that blend the virtual world with the real world. Unlike vr, which completely replaces your surroundings, ar enhances your environment by adding virtual objects and characters to it. Ar applications in the sector are growing fast.
Imagine playing a strategy game where the battlefield unfolds on your living room table, or exploring a haunted house where ghosts appear to float through your walls. Ar glasses allow users to interact with virtual objects and characters in their real environment, creating a more engaging and believable experience. This opens up new possibilities for interactive storytelling, location-based gaming, and social entertainment. Ar and vr are starting to blend together more and more.
Despite their potential, current ar glasses still face several limitations that hinder their widespread adoption. Addressing these challenges is crucial for unlocking the full potential of augmented reality.
Bulk and Weight: Many glasses today are still too bulky and heavy to be worn comfortably for extended periods.
Solution: Ongoing advancements in miniaturization and materials science are leading to lighter and more compact designs.
Limited Field of View: The field of view of many ar glasses is still relatively narrow, making the augmented reality experience feel constrained. Typical ar glasses have a 50-degree field of view.
Solution: Researchers are exploring new optics technologies, such as waveguides and diffractive optics, to expand the field of view without increasing the size or weight of the glasses.
Battery Life: Smart glasses need sufficient battery life to be practical for everyday glasses use.
Solution: Improving battery technology and optimizing power consumption are essential for extending the battery life of ar glasses.
Display Quality: The brightness, contrast, and resolution of ar displays still need improvement to create a truly seamless and immersive experience.
Solution: Advancements in micro-display technologies, such as oled and microLED, are improving the image quality and power efficiency of ar displays.
Social Acceptability: Some people may feel self-conscious about wearing ar glasses in public.
Solution: Designing ar glasses that are stylish and discreet can help to improve their social acceptability.
Overcoming these limitations will pave the way for ar glasses to become a mainstream technology.
The future of augmented reality looks incredibly promising, with ar smart glasses poised to become an integral part of our daily lives. As the technology continues to mature, we can expect to see significant advancements in several areas:
Improved Hardware: Ar glasses will become smaller, lighter, more powerful, and more energy-efficient.
Enhanced Software: Ar software will become more intelligent, intuitive, and context-aware, providing users with personalized and relevant information.
Seamless Integration: Ar glasses will seamlessly integrate with other devices and services, creating a connected ecosystem that enhances our productivity and entertainment.
Wider Adoption: Ar glasses will become more affordable and accessible, leading to widespread adoption across various industries and consumer markets.
New Applications: We can expect to see new and innovative applications of ar emerge in areas such as education, healthcare, manufacturing, retail, and entertainment.
Augmented reality has the potential to transform the way we interact with the world, and ar glasses are the key to unlocking that potential.
As augmented and virtual reality technologies converge, xr glasses are emerging as a promising new category of wearable devices. "XR" stands for "Extended Reality" and encompasses ar, vr, and everything in between. XR glasses aim to provide a more versatile and adaptable experience than either ar or vr alone.
While ar glasses focus on augmenting the real environment with digital information, and vr headsets create completely virtual worlds, xr glasses allow users to seamlessly transition between these realities. They may be able to switch between ar and vr modes on demand, or even create blended realities that combine elements of both. The precise form factor and capabilities of xr glasses are still evolving, but they represent an exciting step towards a more unified and immersive computing experience.
AR glasses blend digital information with the physical world.
They differ from VR headsets, which create completely virtual worlds.
Core components include displays, processors, sensors, and cameras.
Optics and displays project images onto the user's field of view.
Sensors track movement and surroundings for accurate augmented reality.
Practical applications span manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, and more.
AR glasses are enhancing gaming and entertainment experiences.
Limitations include bulk, field of view, battery life, and social acceptability.
The future of augmented reality is bright, with advancements in hardware and software.
XR glasses are emerging as a versatile bridge between ar and vr.
Contact: Ashley Wu
Phone: +86 17773983073
E-mail: [email protected]
Add: 708 Room A Buiding Huafeng International Robot Industrial Park Xixiang Bao'an