When it comes to virtual reality (VR) displays, the choice between OLED and LCD technology is crucial for an immersive experience. This article delves into the advantages and disadvantages of OLED and LCD VR displays, helping you understand which technology might be best for your needs. As VR continues to evolve, knowing the differences in display technology can enhance your viewing experience significantly. Read on to explore the nuances of OLED vs. LCD and discover the best VR display options available today.
1. What is VR and Why Does Display Technology Matter?
2. What Are OLED Displays?
3. What Are LCD Displays?
4. OLED vs. LCD: What Are the Key Differences?
5. How Does Micro OLED Technology Fit In?
6. What Are the Advantages of OLED in VR?
7. What Are the Disadvantages of OLED in VR?
8. What Are the Advantages of LCD in VR?
9. What Are the Disadvantages of LCD in VR?
10. Which Is the Best VR Display for You?
Virtual reality (VR) immerses users in a digital environment, requiring high-quality displays to create a convincing experience. The type of display technology used directly impacts visual quality, refresh rates, and overall immersion. Understanding the differences between OLED and LCD displays is essential for anyone looking to invest in VR technology.
Quality display technology can enhance the realism of the VR experience, making it feel more engaging and lifelike. This article will guide you through the essential aspects of each technology, helping you make an informed decision based on your personal needs and preferences.
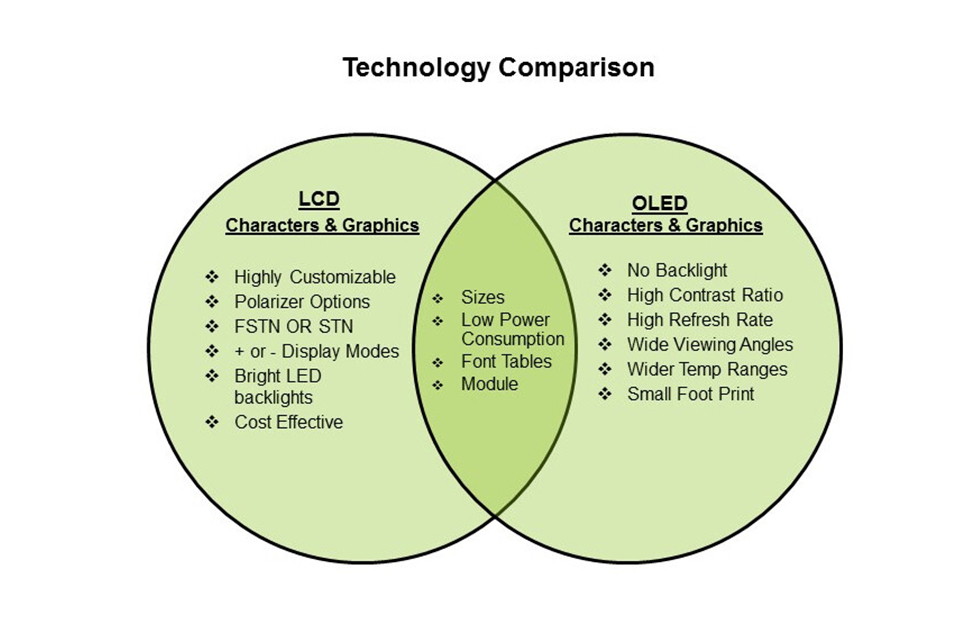
Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) displays are renowned for their vibrant colors and deep blacks. Unlike LCDs, OLEDs generate light on their own, allowing for more precise control over brightness and contrast. This capability results in stunning visuals that can significantly enhance the VR experience.
In an OLED display, each pixel emits its own light, which means that when a pixel is turned off, it appears completely black. This feature leads to an impressive contrast ratio, making colors appear more vivid. As a result, OLED technology is often favored in high-end VR headsets, where visual fidelity is paramount.
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) technology, on the other hand, relies on a backlight to illuminate the pixels. While LCDs have improved significantly over the years, they generally struggle to achieve the same level of contrast as OLEDs. However, advancements like fast LCD panels and Quantum Dot technology have made LCD displays more competitive in the VR space.
LCDs are known for their brightness and color accuracy, making them suitable for various applications beyond VR. They tend to be more cost-effective than OLED displays, which can be a significant consideration for budget-conscious consumers.
When comparing OLED and LCD, several factors come into play, such as color accuracy, response time, and viewing angles.
· Color Accuracy: OLED displays typically offer superior color performance due to their ability to produce true blacks and vibrant colors.
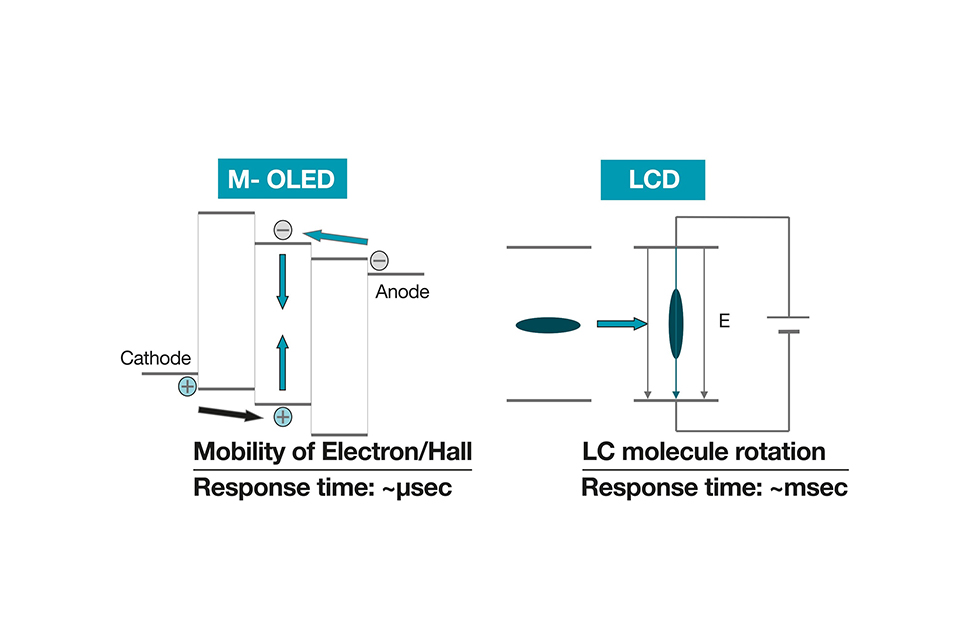
· Response Time: OLEDs have faster response times, which is crucial for VR applications where motion blur can detract from the experience.
· Viewing Angles: OLED technology generally provides better viewing angles, allowing for a consistent image quality from different perspectives.
In contrast, LCD displays often excel in brightness and are less prone to screen burn-in, a common issue with OLED technology. Each display type has its unique strengths and weaknesses, making the choice dependent on the user's specific needs.
Micro OLED is a cutting-edge display technology that combines the advantages of OLED with a compact form factor. This technology is particularly suited for VR headsets, providing high pixel density and excellent visual quality in a lightweight design.
Micro OLED displays deliver stunning resolution and color depth, making them ideal for immersive VR experiences. They offer the same benefits as traditional OLEDs, such as deep blacks and vibrant colors, but with enhanced efficiency and a smaller footprint, which is crucial for portable VR devices.
1. Superior Contrast and Color: OLED displays offer unmatched contrast ratios and color accuracy, enhancing the overall visual experience in VR.
2. Faster Response Times: With quicker pixel response times, OLEDs minimize motion blur, which is essential for fast-paced VR games and experiences.
3. Improved Immersion: The ability to display true blacks allows users to feel more immersed in the virtual environment, enhancing the realism of the experience.
These advantages make OLED a popular choice for high-end VR headsets, where visual fidelity is a top priority.
1. Screen Burn-In: One of the most significant drawbacks of OLED technology is the potential for screen burn-in, where static images can leave a permanent mark on the display.
2. Higher Cost: OLED displays are generally more expensive to produce, leading to higher retail prices for VR headsets that utilize this technology.
3. Limited Brightness: While OLEDs excel in contrast, they may struggle in extremely bright environments compared to LCDs.
These disadvantages should be considered when deciding whether an OLED VR headset is the right choice for you.
1. Cost-Effectiveness: LCD displays are usually less expensive than OLEDs, making them a more budget-friendly option for consumers.
2. Brightness: LCD technology can achieve higher brightness levels, making them suitable for well-lit environments.
3. No Burn-In Issues: Unlike OLEDs, LCDs do not suffer from burn-in, providing a more durable option for long-term use.
These advantages make LCDs appealing for certain applications, especially for those who prioritize affordability and longevity over absolute visual quality.
1. Lower Contrast Ratios: LCD displays typically cannot achieve the same level of contrast as OLEDs, which can affect the depth of colors and overall immersion.
2. Slower Response Times: While advancements have been made, LCDs generally have slower response times, which can result in motion blur during fast-paced actions in VR.
3. Narrower Viewing Angles: LCDs can exhibit color shifts and reduced brightness when viewed from angles other than straight on.
These disadvantages can impact the user experience in VR, particularly in situations where visual fidelity is critical.
Choosing between OLED and LCD for VR ultimately depends on your specific needs and preferences. If you prioritize visual quality, fast response times, and immersion, an OLED display may be the best choice. However, if you are looking for a more affordable option with good brightness and no burn-in issues, an LCD display could be more suitable.
It’s essential to consider the types of VR experiences you’ll be engaging in. For instance, if you enjoy fast-paced gaming, the advantages of OLED might outweigh the disadvantages. Conversely, for casual viewing or experiences in bright environments, an LCD could be perfectly adequate.
· OLED displays offer superior contrast and vibrant colors, ideal for immersive VR experiences.
· LCD displays are more cost-effective, brighter, and free from burn-in issues.
· The choice between OLED and LCD depends on personal preferences, budget, and the specific VR applications you intend to use.
In conclusion, both OLED and LCD technologies have their merits in the VR space. Understanding their differences can help you make an informed decision, ensuring you choose the best VR display for your needs.
Contact: Ashley Wu
Phone: +86 17773983073
E-mail: [email protected]
Add: 708 Room A Buiding Huafeng International Robot Industrial Park Xixiang Bao'an