Microdisplays are small, high-resolution screens that are revolutionizing the way we interact with technology. From OLED microdisplays to LCD-based microdisplays, these compact screens are used in a variety of applications, including virtual reality (VR) headsets, augmented reality (AR) glasses, camera viewfinders, and wearable devices. But what exactly is a microdisplay output, and why is it so important? This article explores the fundamentals of microdisplays, their technology, and their potential applications, helping you understand why they are a critical component in modern display systems.
What is a Microdisplay?
Defining Microdisplays: What makes them unique?
How Do Microdisplays Work?
What Are the Types of Microdisplays?
OLED Microdisplays
LCD Microdisplays
What is Microdisplay Output?
Understanding Output in Microdisplays
Factors That Affect Microdisplay Output
How Do OLED Microdisplays Work?
The Role of Organic Light Emitting Diodes (OLEDs)
Advantages of OLED Microdisplays
What is the Role of Pixels in Microdisplays?
Pixel Density and Resolution
How Pixel Uniformity Impacts Image Quality
How Does Brightness Impact Microdisplay Output?
Brightness Levels in OLED and LCD Microdisplays
Why Brightness Matters for AR and VR Applications
What Are the Potential Applications of Microdisplays?
AR and VR Devices
Wearables and Smart Glasses
Medical and Industrial Uses
How Do Microdisplays Compare to Traditional Displays?
Size and Efficiency
Performance in High-Resolution Applications
What Are the Challenges of Microdisplay Technology?
Technical Limitations
Cost and Scalability
The Future of Microdisplay Technology
Emerging Trends in Microdisplays
How Microdisplays Will Shape the Future of Displays
Microdisplays are small, high-resolution screens typically measuring less than 1 inch diagonally. Despite their size, they deliver exceptional image quality, making them ideal for applications where space is limited but performance is critical.How Do Microdisplays Work? Microdisplays use advanced technologies like OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diodes) or LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) to produce sharp, vibrant images. These displays are often paired with optical systems, such as lenses or magnifiers, to project the image into the user’s field of view.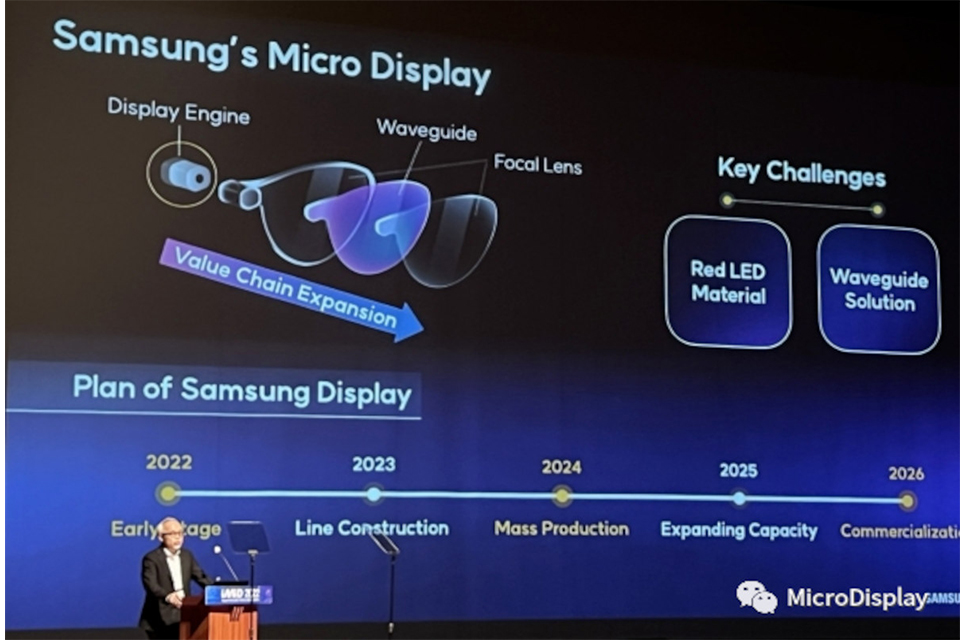
1. OLED Microdisplays: OLED microdisplays use organic light-emitting diodes to produce light and color. They are self-emissive, meaning each pixel generates its own light, resulting in deep blacks, high contrast, and vibrant colors.2. LCD Microdisplays: LCD microdisplays rely on a backlight to illuminate the screen. While they are less expensive than OLEDs, they typically have lower contrast ratios and less vibrant colors.
Understanding Output in Microdisplays: The output of a microdisplay refers to the quality and performance of the image it produces. This includes factors like resolution, brightness, color accuracy, and uniformity.Factors That Affect Microdisplay Output:
Pixel Density: Higher pixel density results in sharper images.
Brightness: Determines visibility in different lighting conditions.
Contrast Ratio: Impacts the depth and vibrancy of colors.
Uniformity: Ensures consistent image quality across the display.
The Role of Organic Light Emitting Diodes (OLEDs): OLED microdisplays use organic materials that emit light when an electric current passes through them. This eliminates the need for a backlight, allowing for thinner and more energy-efficient displays.Advantages of OLED Microdisplays:
Deep Blacks: OLED pixels can turn off completely, achieving true blacks.
High Contrast: Superior contrast ratios enhance image quality.
Energy Efficiency: Consumes less power, especially for dark content.
Pixel Density and Resolution: Pixel density, measured in pixels per inch (PPI), determines the sharpness of the image. Microdisplays often have extremely high pixel densities, making them ideal for AR and VR applications where clarity is essential.How Pixel Uniformity Impacts Image Quality: Uniformity ensures that all pixels perform consistently, avoiding issues like brightness variations or color shifts that can degrade the viewing experience.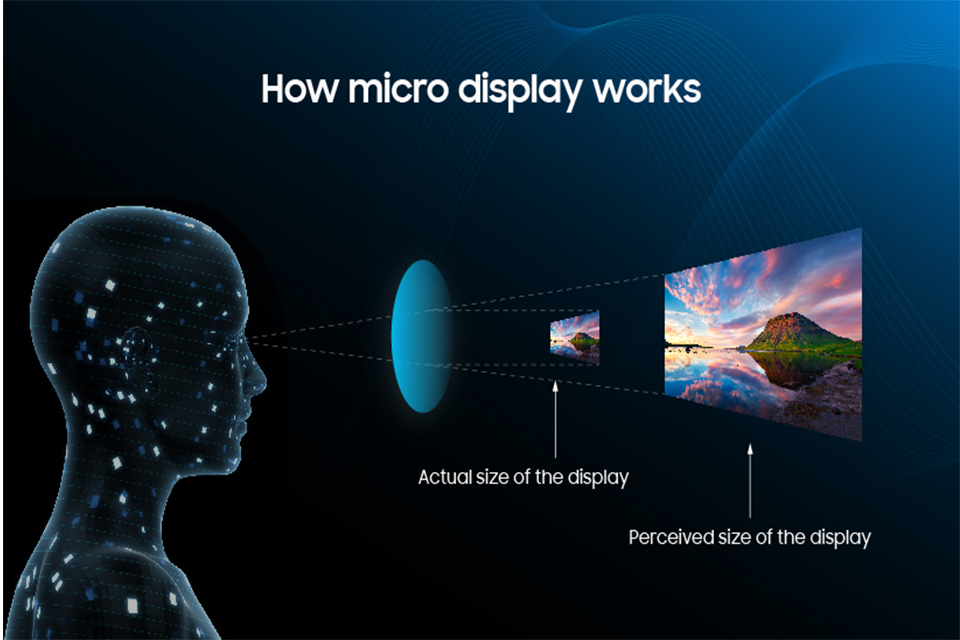
Brightness Levels in OLED and LCD Microdisplays:
OLED Microdisplays: Typically have lower brightness levels but excel in contrast and color accuracy.
LCD Microdisplays: Offer higher brightness, making them suitable for outdoor use.
Why Brightness Matters for AR and VR Applications: In AR and VR devices, brightness is crucial for visibility, especially in environments with high ambient light. A brighter display ensures that digital content remains clear and legible.
1. AR and VR Devices: Microdisplays are the backbone of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) headsets, providing the high resolution and low latency needed for immersive experiences.2. Wearables and Smart Glasses: Microdisplays enable compact, lightweight designs for smart glasses and other wearable devices, delivering information directly to the user’s field of view.3. Medical and Industrial Uses: In medical imaging and industrial equipment, microdisplays provide precise visuals for tasks like surgery, diagnostics, and machine operation.
Size and Efficiency: Microdisplays are significantly smaller than traditional displays, making them ideal for compact devices. They also consume less power, extending battery life in portable applications.Performance in High-Resolution Applications: Microdisplays excel in delivering high-resolution images, making them superior to traditional displays for applications like AR/VR headsets and camera viewfinders.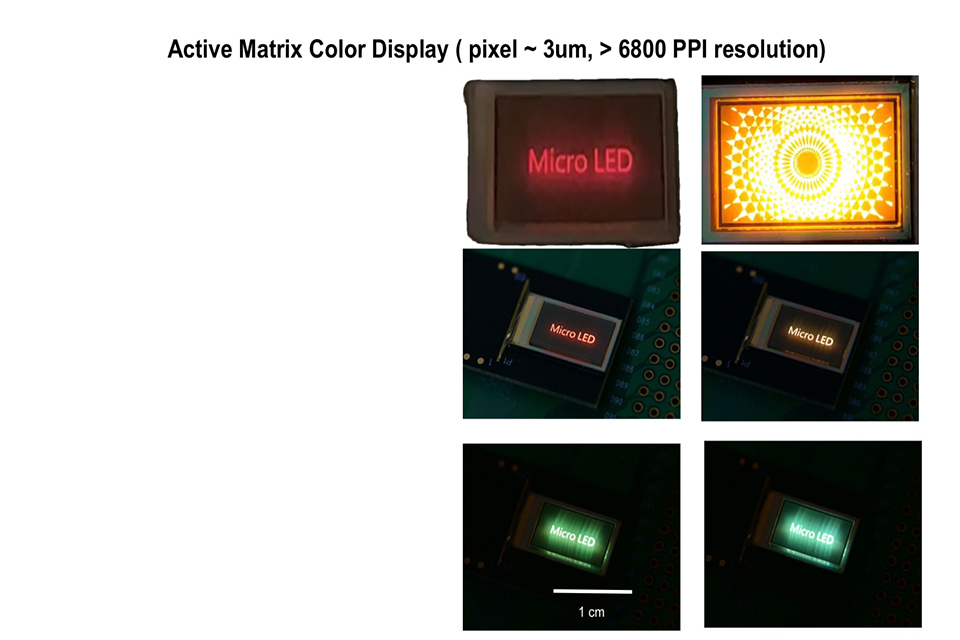
Technical Limitations:
Brightness: OLED microdisplays often struggle with brightness levels, limiting their use in outdoor environments.
Manufacturing Complexity: Producing high-resolution microdisplays requires advanced manufacturing techniques.
Cost and Scalability: Microdisplays are more expensive to produce than traditional displays, which can limit their adoption in budget-friendly devices.
Emerging Trends in Microdisplays:
Micro OLED: Advancements in OLED technology are enabling even smaller, more efficient displays.
Transparent Displays: Microdisplays with transparency are being developed for AR applications.
Higher Resolutions: 4K and beyond are becoming standard for microdisplays in premium devices.
How Microdisplays Will Shape the Future of Displays: As technology advances, microdisplays will play a critical role in wearables, AR/VR devices, and medical imaging, driving innovation across industries.
Microdisplays are small, high-resolution screens used in AR/VR headsets, smart glasses, and medical devices.
The two main types of microdisplays are OLED microdisplays and LCD microdisplays, each with unique advantages.
Microdisplay output is determined by factors like resolution, brightness, and pixel uniformity.
Applications include AR/VR, wearables, and industrial equipment, where compact size and high performance are essential.
Challenges include brightness limitations and high production costs, but advancements in technology are addressing these issues.
The future of microdisplays lies in higher resolutions, transparent designs, and expanded use in emerging technologies.
Microdisplays are at the forefront of innovation, enabling the next generation of immersive and portable devices. As their capabilities continue to grow, they will redefine how we interact with technology in our daily lives.
Contact: Ashley Wu
Phone: +86 17773983073
E-mail: [email protected]
Add: 708 Room A Buiding Huafeng International Robot Industrial Park Xixiang Bao'an