When it comes to display technologies, the debate between LCoS (Liquid Crystal on Silicon) and OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) is both fascinating and crucial for consumers and professionals alike. This article delves into the key differences between these two prominent display types, providing insights into their unique technologies, advantages, and applications. Understanding these differences is essential for making informed decisions about which display technology best suits your needs, whether for home entertainment, professional presentations, or wearable devices.
Article Outline
1. What is LCoS Technology?
Definition and basic principles of LCoS.
How LCoS works in projectors.
2. What is OLED Technology?
Overview of OLED technology and its functioning.
Comparison to traditional LCD.
3. LCoS vs. OLED: Key Differences
Fundamental differences in technology.
Performance metrics comparison.
4. Advantages of LCoS Displays
Benefits of using LCoS in projectors and microdisplays.
Real-world applications of LCoS.
5. Advantages of OLED Displays
Why OLEDs are favored in modern devices.
Specific advantages in color accuracy and contrast.
6. LCoS Projectors: How Do They Work?
Detailed look at LCoS projectors.
Comparison with DLP (Digital Light Processing) projectors.
7. OLED Microdisplays in Wearable Technology
The role of OLED microdisplays in AR (Augmented Reality).
Advantages in wearability and battery life.
8. LCoS vs. DLP: Which is Better?
Analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of LCoS and DLP.
Use cases for both technologies.
9. The Future of Display Technologies
Trends in LCoS and OLED development.
Predictions for the future of microLED and MEMS technologies.
10. Conclusion: Choosing the Right Display Technology
Summary of key points.
Guidance for selecting between LCoS and OLED based on needs.
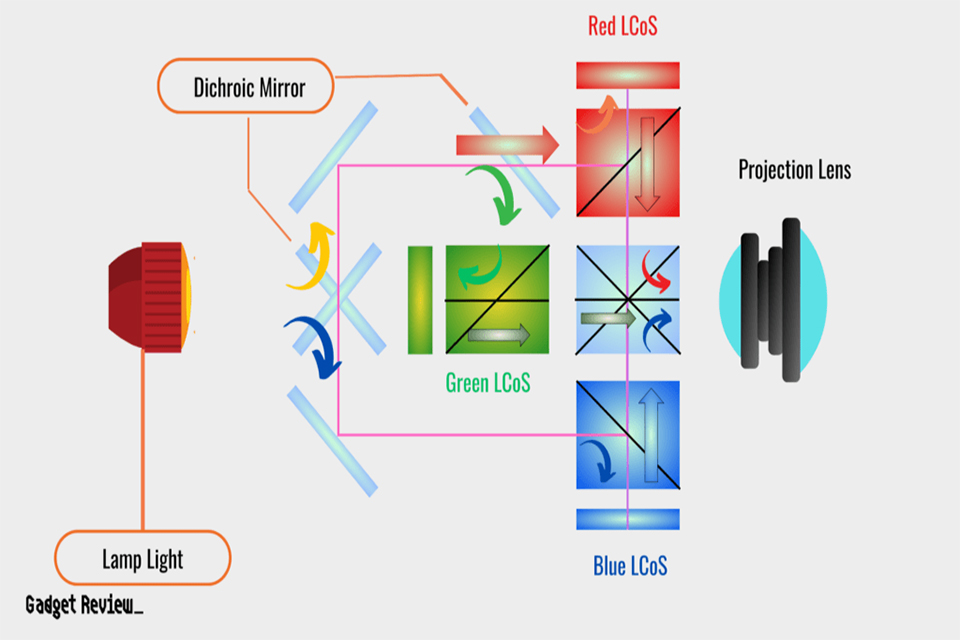
LCoS, or Liquid Crystal on Silicon, is a display technology that utilizes liquid crystals applied to a silicon backing. This innovative approach allows for high-resolution images and is commonly used in projectors and microdisplays. Unlike traditional LCDs that rely on a backlight, LCoS displays modulate light directly from the silicon chip, resulting in sharper images and better contrast.
LCoS technology is particularly favored in the realm of projectors, where it excels in delivering high-quality visuals with minimal pixelation. This capability makes LCoS projectors ideal for professional environments where image clarity is paramount, such as in business presentations or cinema settings.
OLED, or Organic Light Emitting Diode, is a display technology characterized by its use of organic compounds that emit light when an electric current is applied. This allows each pixel to produce its own light, eliminating the need for a backlight and enabling deeper blacks and richer colors compared to traditional LCDs.
The ability of OLED displays to achieve high contrast ratios and vibrant colors has made them popular in consumer electronics, particularly in televisions and smartphones. Additionally, the flexibility of OLED technology allows for thinner and more lightweight designs, making it an excellent choice for wearable devices and AR displays.
When comparing LCoS and OLED, the fundamental differences lie in their underlying technologies. LCoS requires a reflective surface, while OLED is emissive, meaning it generates its own light. This distinction results in different performance metrics, such as brightness, contrast, and color accuracy.
In terms of brightness, LCoS projectors can achieve very high levels, making them suitable for well-lit environments. Conversely, OLED displays excel in dimmer settings, where their ability to turn off individual pixels results in true blacks and exceptional color depth.
LCoS displays offer several advantages, particularly in projector technology. One of the primary benefits is their high resolution and pixel density, which provide sharp images even at larger sizes. Additionally, LCoS projectors are known for their excellent color reproduction and minimal motion blur, making them ideal for video presentations.
In practical applications, LCoS technology is commonly used in high-end projectors for home theaters and professional venues. Its ability to produce large, clear images without distortion makes it a preferred choice for cinematic experiences.
OLED displays come with a range of advantages that make them highly sought after in various applications. One of the standout features of OLED technology is its exceptional color accuracy. Because each pixel emits its own light, OLEDs can achieve vibrant colors that are often more true-to-life than those produced by LCoS or LCD displays.
Moreover, OLEDs have faster response times, which enhances the viewing experience in fast-paced content like gaming or action films. The lack of a backlight also contributes to lower power consumption, especially in portable devices, making OLED a sustainable choice for modern technology.
LCoS projectors function by reflecting light off a silicon chip coated with liquid crystals. As light passes through these crystals, it is modulated to create images. This unique method allows for high resolution and detailed visuals, which are critical for applications like movie screenings or business presentations.
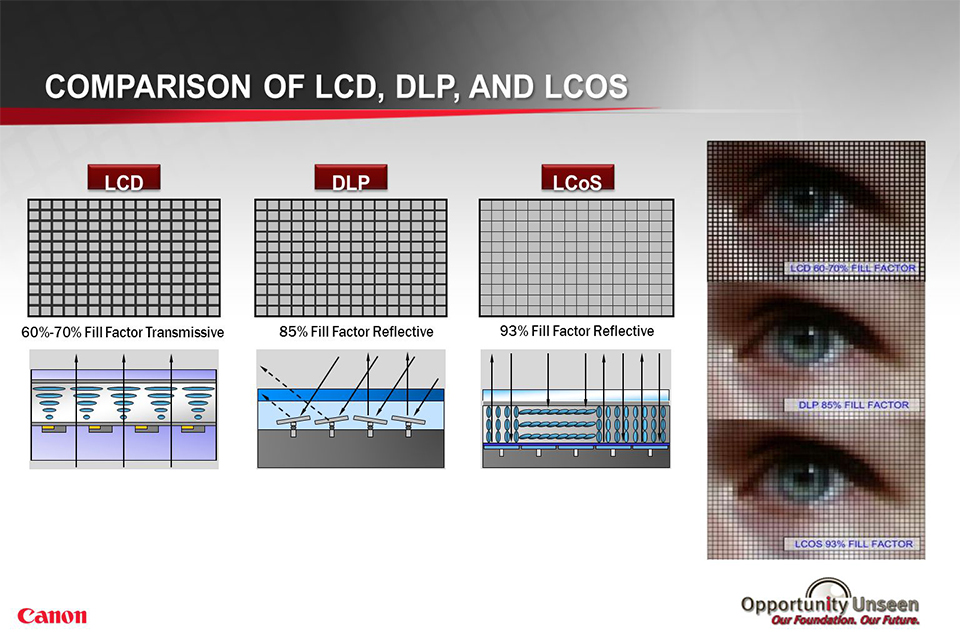
In comparison to DLP projectors, LCoS projectors tend to offer better color accuracy and smoother images due to their higher native resolution. While DLP may excel in brightness, LCoS shines in delivering true-to-life colors and fine detail, making it a strong contender in the projector market.
The integration of OLED microdisplays in wearable technology, particularly in AR devices, has revolutionized the field. OLED's lightweight and compact design allows for high-resolution displays that can be comfortably worn for extended periods. The self-emissive nature of OLED technology means that users experience bright, vivid images even in challenging lighting conditions.
Moreover, OLED microdisplays offer improved battery efficiency, which is crucial for wearable devices that require long operational times without frequent charging. This technology not only enhances the user experience but also paves the way for more advanced applications in augmented and virtual reality.
When weighing LCoS against DLP, it is essential to consider the intended use. LCoS projectors are often preferred in environments where color fidelity and image clarity are critical, such as home theaters. On the other hand, DLP projectors may be more suitable for portable applications due to their typically lighter weight and higher brightness levels.
Ultimately, the choice between LCoS and DLP will depend on specific needs, such as the environment and desired image quality. For those prioritizing color accuracy and detail, LCoS is likely the better option, while DLP may serve well in situations requiring portability and brightness.
The future of display technologies looks promising, with both LCoS and OLED continuing to evolve. Advances in microLED and MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) technology are expected to further enhance the capabilities of displays, offering even greater resolution and efficiency.
As consumer demand for high-quality visuals grows, manufacturers are investing in research and development to refine these technologies. The integration of AI to optimize display performance and energy consumption is expected to be a game-changer in how displays are used across various industries.
In conclusion, both LCoS and OLED display technologies have unique strengths and applications. LCoS is ideal for situations requiring high resolution and color fidelity, particularly in projection environments. Conversely, OLED offers flexibility and efficiency, making it a top choice for personal devices and wearables.
When deciding between LCoS and OLED, consider your specific needs, such as the intended use, environment, and desired visual quality. By understanding the unique features of each technology, you can make an informed decision that best suits your requirements.
LCoS: High resolution, excellent color accuracy, ideal for projectors.
OLED: Vibrant colors, self-emissive technology, great for portable devices.
LCoS Projectors: Best for high-definition viewing in professional settings.
OLED Microdisplays: Perfect for wearables and AR applications.
Future Trends: Advances in microLED and MEMS technologies promise even better displays.

By understanding the distinctions between LCoS and OLED, you can choose the right display technology for your needs, ensuring a fulfilling visual experience.
Contact: Ashley Wu
Phone: +86 17773983073
E-mail: [email protected]
Add: 708 Room A Buiding Huafeng International Robot Industrial Park Xixiang Bao'an