Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), Extended Reality (XR), and Mixed Reality (MR) are terms that frequently pop up in discussions about modern technology. Understanding the differences and overlaps between these technologies is essential for anyone interested in the future of digital experiences. This article breaks down each of these technologies, explains their unique characteristics, and explores their applications, helping you grasp how they might impact our lives. By the end, you'll have a clear understanding of how AR, VR, XR, and MR compare, and why this knowledge is crucial in today's tech-driven world.
1. What is XR and Why is it Important?
2. How Does AR Work and What Are Its Applications?
3. Understanding VR: What Can You Experience?
4. What is the Role of MR in Blending Realities?
5. How Do AR and VR Compare in Gaming?
6. What Are Real-World Uses for XR Experiences?
7. How Does Technology Enable Mixed Reality?
8. What is the Difference Between VR and MR?
9. Why is Extended Reality Considered an Umbrella Term?
10. What is the Future of AR, VR, XR, and MR Technologies?
Extended Reality (XR) is an umbrella term that encompasses all immersive technologies, including AR, VR, and MR. It represents a convergence of the virtual and real worlds, enabling users to interact with both physical and digital elements seamlessly. XR is important because it opens up new avenues for innovation across various sectors, from gaming and entertainment to education and healthcare.
XR experiences are increasingly being adopted in industries looking to enhance user engagement and improve training processes. For instance, businesses are utilizing XR to create simulations that allow employees to practice skills in a safe environment. This not only boosts confidence but also enhances learning outcomes.
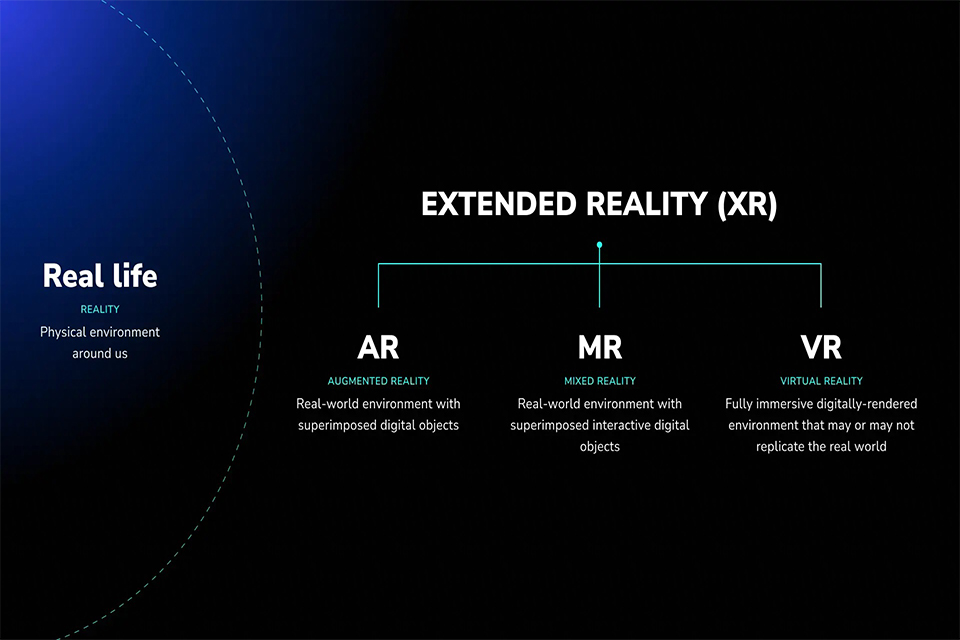
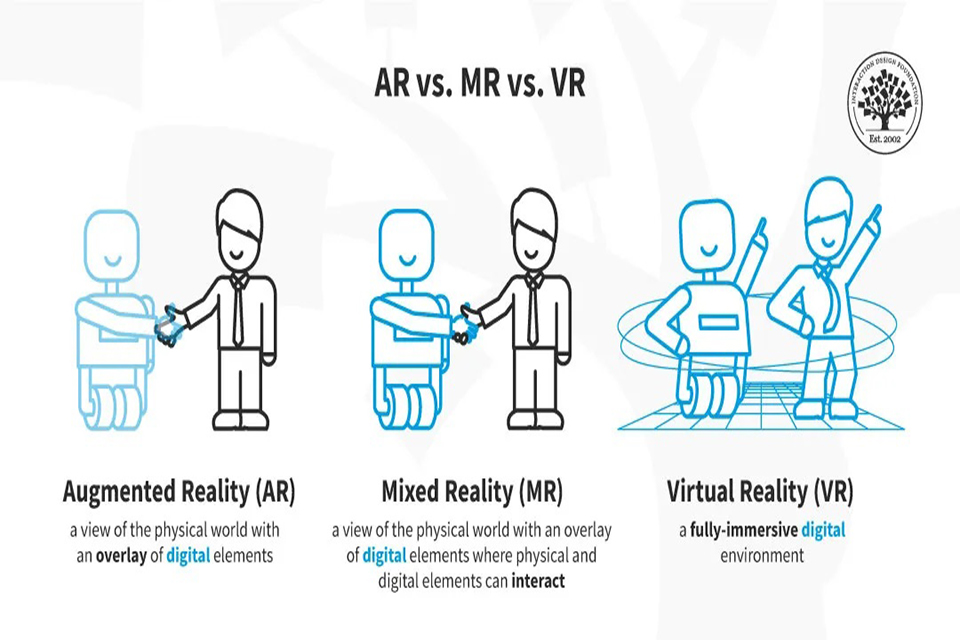
Augmented Reality (AR) overlays digital elements onto the real world, allowing users to interact with both simultaneously. AR technology works by using devices like smartphones or AR glasses to recognize physical objects and then display relevant digital information. One popular example is the mobile game Pokémon GO, where players see Pokémon overlaid on real-world locations through their screens.
AR has applications beyond gaming; it is increasingly being used in fields like retail, where customers can visualize how products will look in their homes before making a purchase. Apps that allow users to place virtual furniture in their living rooms are a prime example of AR in action.
Virtual Reality (VR) immerses users in a completely digital environment, isolating them from the physical world. This is typically achieved through VR headsets that track head movements and provide 360-degree visuals. Users can explore virtual worlds, interact with 3D objects, and experience scenarios that would be impossible in real life.
The experiences in VR can range from gaming, where players can step into their favorite game worlds, to educational simulations, where students can explore the solar system or dive into the human body. VR is transforming how we consume media, making experiences more interactive and engaging.
Mixed Reality (MR) combines elements of both AR and VR, allowing users to interact with both real and virtual objects in real time. MR technologies enable digital objects to coexist and interact with the physical environment, creating a richer and more immersive experience. For example, Microsoft’s HoloLens allows users to manipulate holograms while still being aware of their real surroundings.
MR has significant potential in fields like architecture and design, where professionals can visualize and interact with their projects in a real-world context. This capability allows for better collaboration and decision-making, as stakeholders can see and discuss changes in real time.
When comparing AR and VR in gaming, the key difference lies in the level of immersion. AR enhances the real world by adding digital elements, while VR creates a completely virtual environment. This distinction influences gameplay; AR games often require players to be aware of their surroundings, while VR games can provide a more immersive experience but may limit physical movement.
Both technologies offer unique gaming experiences. AR games, like Pokémon GO, encourage players to explore their environment, while VR games, such as Beat Saber, provide a fully immersive experience where players can lose themselves in the game world. Understanding these differences helps developers create games that best utilize the strengths of each platform.
XR experiences have practical applications across various industries. In healthcare, AR can assist surgeons by overlaying vital information during procedures, while VR can be used for patient therapy and rehabilitation. In education, XR technologies can enhance learning by providing interactive lessons that engage students in ways traditional methods cannot.
Moreover, in the corporate world, training programs utilizing XR can simulate real-world scenarios for employees, improving retention and application of skills learned. The versatility of XR allows it to be tailored for specific needs, making it a valuable tool in many fields.
The enabling technologies for Mixed Reality include advanced sensors, computer vision, and artificial intelligence. These technologies work together to understand and interpret the real world, allowing digital elements to interact meaningfully with their environment. For example, spatial mapping allows MR devices to recognize surfaces and objects, enabling digital content to be placed accurately in the physical space.
As MR technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more sophisticated experiences that blend physical and digital realms seamlessly. This advancement opens up possibilities for new applications in entertainment, training, and beyond.
While both VR and MR involve digital elements, the primary difference lies in user immersion and interaction with the physical world. VR isolates users in a completely virtual environment, while MR allows for interaction with both real and virtual objects. This means that in MR, users can manipulate digital elements while still being aware of their surroundings, providing a unique blend of experiences.
Understanding this difference is crucial for developers and users alike, as it impacts how these technologies can be utilized in various applications. MR's ability to integrate real-world interactions makes it a powerful tool for collaboration and innovation.
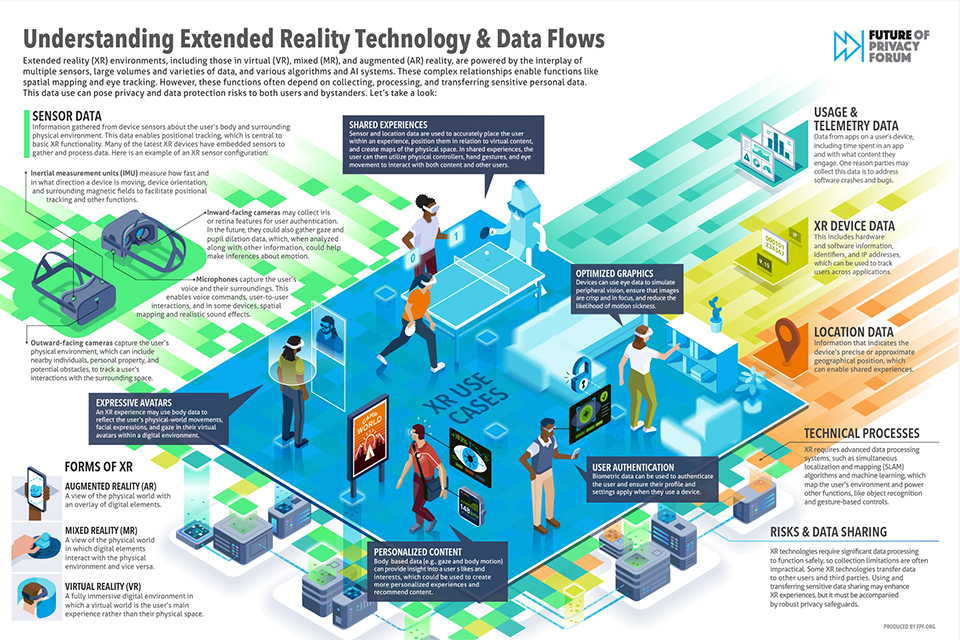
Extended Reality (XR) is considered an umbrella term because it encompasses all forms of immersive technologies, including AR, VR, and MR. This broad definition allows for a better understanding of how these technologies relate to one another and their collective impact on various industries. By viewing XR as an umbrella term, we can appreciate the interconnectedness of these technologies and their potential to transform experiences across different fields.
This perspective encourages innovation, as developers can explore how different technologies can work together to create more immersive and engaging experiences. Understanding XR as a cohesive category helps stakeholders navigate the rapidly evolving landscape of immersive technology.
The future of AR, VR, XR, and MR technologies is promising, with advancements in hardware and software driving innovation. As devices become more affordable and accessible, we can expect broader adoption across various sectors. The integration of AI and machine learning will further enhance these technologies, making experiences more personalized and intuitive.
Moreover, as remote work continues to rise, XR technologies will play a crucial role in facilitating collaboration and communication. The possibilities are endless, and staying informed about these developments will be essential for anyone interested in the future of technology.
· XR is an umbrella term for AR, VR, and MR, representing a convergence of real and digital worlds.
· AR enhances the real world with digital elements, while VR immerses users in a completely virtual environment.
· MR allows interaction between real and virtual objects, providing a unique blend of experiences.
· Each technology has distinct applications across industries, including healthcare, education, and gaming.
· Understanding these differences can help users and developers harness the full potential of immersive technologies.
By grasping these concepts, readers can better appreciate the transformative potential of AR, VR, XR, and MR in shaping our future.
Contact: Ashley Wu
Phone: +86 17773983073
E-mail: [email protected]
Add: 708 Room A Buiding Huafeng International Robot Industrial Park Xixiang Bao'an