Extended Reality (XR) is rapidly transforming how we interact with technology and the world around us. This article explores the multifaceted realm of XR, encompassing virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR). From immersive experiences to practical applications, we'll delve into the technologies, devices, and potential future of XR. Read on to discover how XR is revolutionizing industries and reshaping our digital and physical realities.
Extended Reality (XR) is an umbrella term that encompasses all realities that are modified by compute. This includes virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR), as well as any future realities that might emerge. Think of it as a spectrum, with the physical world at one end and completely virtual worlds at the other. XR technologies bridge the gap between these two extremes, enhancing our perception and interaction with information.
The term extended reality xr is used as an umbrella term because it is an all-encompassing label that can adapt to new technologies and innovations in the field. As the industry evolves, XR provides a flexible framework for understanding and categorizing the various types of reality experiences. It allows us to discuss the broader context of immersive technology without getting bogged down in the specifics of each individual type.

The fundamental difference between augmented reality and virtual reality lies in how they interact with the physical world. Augmented reality (AR) enhances the physical world by overlaying digital information onto it. Imagine looking through your smartphone camera and seeing virtual objects placed on top of real objects in your environment. A great example of this is Pokémon GO, where virtual creatures appear overlaid onto the physical world through your phone's screen.
Virtual reality (VR), on the other hand, creates a completely immersive virtual environment that replaces the user's view of the physical world. VR users typically wear a vr headset that displays a computer-generated environment, allowing them to interact with a virtual world. Unlike AR, vr users are fully immersed and cannot see or interact with the real physical world around them without removing the vr headset.
| Feature | Augmented Reality (AR) | Virtual Reality (VR) |
|---|---|---|
| Environment | Enhances the physical world with digital overlays | Creates a completely immersive virtual environment |
| User View | Sees the real world with digital augmentations | Sees only a computer-generated virtual world |
| Interaction | Interacts with both real and virtual elements | Interacts primarily with virtual elements |
| Examples | Pokémon GO, AR filters on social media | Meta Quest 3, Oculus Rift |
| Accessibility | Often accessible via smartphones and tablets | Requires specialized vr devices like a vr headset |
Mixed reality bridges the gap between AR and VR, offering a more seamless integrate between the real and virtual worlds. Mixed reality not only overlays digital content but also allows virtual objects to interact with real objects in a way that feels natural and intuitive. This requires advanced sensor technology and compute power to accurately map the physical environment and anchor virtual elements within it.
Mixed reality is achieved through a combination of technologies, including:
Advanced Sensors: Sensors are used to map the physical environment in real-time.
Spatial Computing: Spatial computing enables virtual objects to understand and interact with the physical world.
Advanced Display Technology: Advanced display technology presents virtual objects in a way that feels realistic and integrated with the real world.
The taxonomy of mixed reality visualizes this spectrum, with AR and VR as opposite ends and MR occupying the space in between, offering varying degrees of integration between real and virtual worlds.
The xr applications are vast and span across numerous industries. In healthcare, XR is used for surgical training, patient rehabilitation, and medical visualization. In education, xr could replace traditional textbooks with immersive learning experiences. Manufacturing utilizes xr technologies for design, prototyping, and remote collaboration. Retailers use ar and vr to provide virtual try-on experiences and product demonstrations.
Here are a few more examples:
Training and Simulation: XR provides realistic and safe environments for training in high-risk professions, such as aviation, military, and emergency response.
Remote Collaboration: XR facilitates remote collaboration by allowing teams to work together in shared virtual spaces, regardless of their physical location.
Entertainment and Gaming: As previously mentioned, the ways ar and vr transform gaming and entertainment are phenomenal.
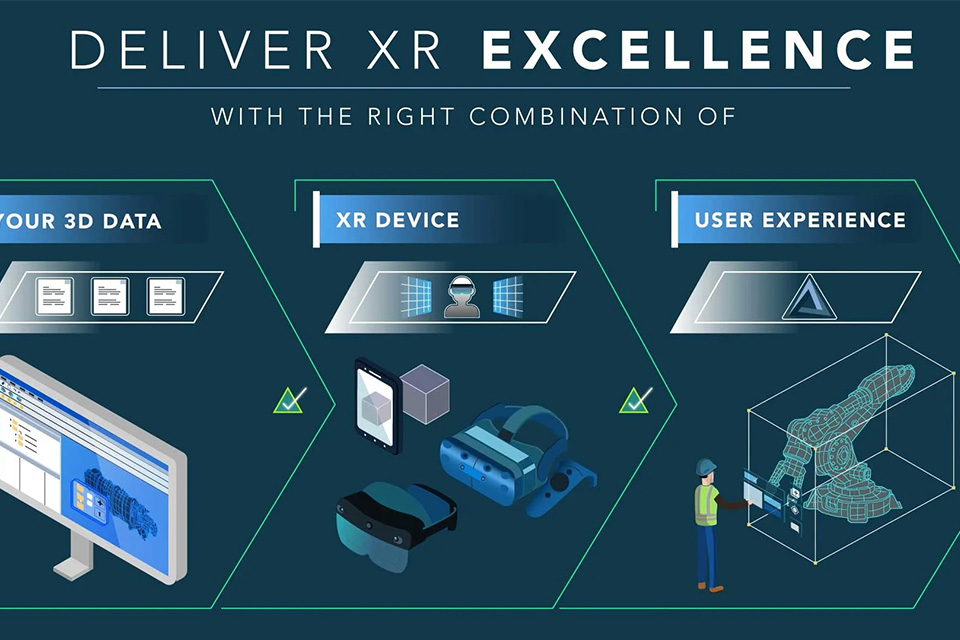
XR devices are the gateway to immersive xr experiences. Vr devices such as head-mounted displays (HMDs) like the Meta Quest 3 and Oculus Rift provide a completely immersive virtual environment by blocking out the user's view of the physical world. These vr devices typically feature high-resolution displays, spatial audio, and motion tracking to enhance the immersive experience.
Smartphones, on the other hand, are commonly used for AR experiences. Through the smartphone's camera and display, ar applications overlay digital content onto the user's view of the real world. While not as immersive as VR, smartphone-based AR offers a convenient and accessible way to use ar in daily life. Ar glasses are also emerging as a popular form factor for AR, offering a more hands-free and seamless AR experience.
Compute power is essential for creating compelling and real-time xr experiences. High-performance processors and graphics cards are needed to render complex 3D environments, process sensor data, and run sophisticated algorithms for tracking and interaction. The amount of compute power required depends on the complexity of the xr experience.
On-device compute is crucial for delivering low-latency and responsive experiences, especially in mobile computing applications. However, some XR applications offload compute-intensive tasks to the cloud to reduce the workload on the xr devices. The trend toward mobile computing is driving the development of more efficient and powerful mobile processors that can handle the demands of XR.
Real-time data is critical for creating boundless xr experiences that are dynamic, responsive, and interactive. Real-time data from sensors, cameras, and other sources allows XR systems to track user movements, map the environment, and respond to changes in the physical world. This real-time awareness enables virtual objects to interact with the real world in a natural and seamless way.
For example, eye tracking technology enables XR systems to understand where the user is looking, allowing for gaze-based interaction and foveated rendering (rendering only the area the user is looking at in high resolution). Computer vision algorithms analyze images and videos from cameras to identify objects, track movements, and understand the scene. Machine learning models are used to predict user behavior, optimize performance, and enhance the immersive experience.

Augmented reality and virtual reality are revolutionizing the gaming and entertainment industries by providing new possibilities for interaction, immersion, and storytelling. VR games offer fully immersive virtual environments where players can explore, interact, and compete with others in ways that were never before possible. AR games overlay digital content onto the real world, creating new and exciting ways to play in physical spaces.
Beyond gaming, VR is also being used to create immersive storytelling experiences, virtual concerts, and virtual tourism. AR is enhancing live events by overlaying digital information onto the physical stage, providing audiences with a more interactive and engaging experience. The possibilities for AR and VR in gaming and entertainment are truly limitless.
Achieving seamless and intuitive XR is not without its challenges. One of the biggest challenges is creating xr technologies that are comfortable, affordable, and accessible to a wide range of users. Other challenges include:
Latency: Reducing latency (the delay between user input and system response) is critical for creating a seamless and responsive XR experience.
Field of View: Increasing the field of view of XR displays is essential for enhancing the sense of immersion.
Resolution: Improving the resolution of XR displays is necessary for reducing pixelation and increasing visual fidelity.
Motion Sickness: Minimizing motion sickness is a key challenge for VR, as some users experience nausea and discomfort when using VR headsets.
Content Creation: Developing high-quality and engaging XR content requires specialized skills and tools.
The future of extended reality xr technologies is bright, with ongoing advancements in hardware, software, and content creation. As xr hardware becomes more powerful, affordable, and comfortable, we can expect to see wider adoption of XR across various industries and applications. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) will also play a crucial role in shaping the future of XR, enabling more intelligent, personalized, and immersive experiences.
The integration of XR with other emerging technologies, such as 5G wireless technology, spatial computing, and generative AI, will opens up new possibilities for XR applications. Imagine being able to use xr to design and customize products in a virtual environment before ordering them, or attending virtual meetings where you can interact with colleagues in a realistic and immersive way. XR offers a glimpse into a future where the boundary between the physical and digital realities is blurred, enhancing the immersive experience for users to interact and communicate with the world around them.
AR augments reality: It overlays digital information onto the real world, often through smartphones.
VR immerses you: It creates a completely virtual environment, requiring devices like vr headsets.
MR blends the physical and digital: It allows virtual objects to interact with the real world.
XR has diverse applications: From healthcare to education and entertainment, XR is revolutionizing industries.
Compute power is crucial: It accelerates the development of realistic and responsive xr experiences.
Real-time data enhances immersion: Sensors and computer vision enable seamless interaction.
XR transforms gaming and entertainment: Creating new and exciting ways to play and experience stories.
Challenges remain: Overcoming latency, motion sickness, and content creation are key.
The future is bright: AI, 5G, and spatial computing will further enhance XR's potential.
Stay up to date to new possibilities and evolution of extended reality.
Contact: Ashley Wu
Phone: +86 17773983073
E-mail: [email protected]
Add: 708 Room A Buiding Huafeng International Robot Industrial Park Xixiang Bao'an