In the world of photography, the viewfinder is an essential tool that significantly influences how photographers capture images. This article delves into the importance of viewfinders in cameras, exploring their functionality and benefits. Whether you're a novice or a seasoned photographer, understanding the role of the viewfinder can elevate your photography skills and enhance your creative vision.
What is a Viewfinder?
Why Use a Viewfinder Over an LCD Screen?
What Are the Different Types of Viewfinders?
How Does an Optical Viewfinder Work?
What is an Electronic Viewfinder?
How to Use a Viewfinder Effectively?
How Do Camera Settings Affect Viewfinder Use?
Why Do Photographers Prefer Viewfinders?
How to Change Camera Settings Using the Viewfinder?
What Should You Remember About Viewfinders?
A viewfinder is a crucial component of a camera that allows photographers to frame their shots accurately. It provides a preview of what the camera lens sees, giving you the opportunity to compose your image before capturing it. Understanding the viewfinder's role is essential for anyone looking to improve their photography skills.
The viewfinder is typically located at the top or back of the camera, and its design can vary based on the type of camera. In modern devices, you may find optical viewfinders in DSLRs or electronic viewfinders (EVFs) in mirrorless cameras. Each type serves a distinct purpose and offers unique advantages.
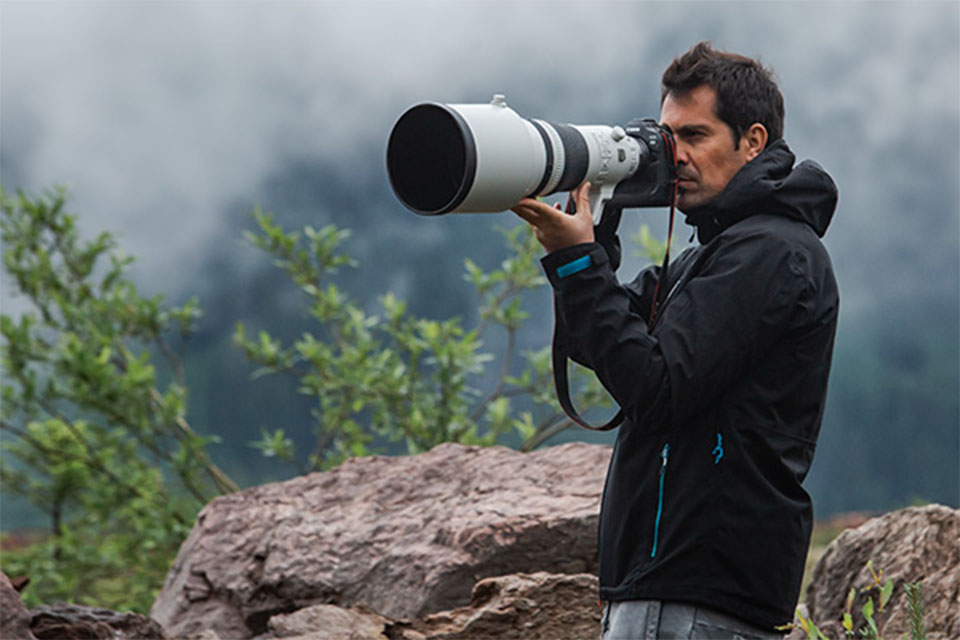

While many cameras feature an LCD screen for framing shots, using a viewfinder can provide several benefits. One of the primary advantages is improved visibility in bright light conditions. When shooting outdoors, sunlight can make it challenging to see the LCD screen clearly. In contrast, a viewfinder allows for a more focused view, reducing glare and enhancing clarity.
Moreover, using a viewfinder can help stabilize your camera. By pressing your eye against the viewfinder, you create a more stable shooting position, which can lead to sharper images, especially in low-light situations. This technique is particularly beneficial for photographers looking to capture fast-moving subjects or intricate details.
There are two main types of viewfinders: optical viewfinders and electronic viewfinders. Understanding the differences between them can help you choose the right camera for your needs.
Optical Viewfinder (OVF): This traditional type uses a series of mirrors and prisms to give you a direct optical view of the scene through the camera lens. OVFs are often found in DSLR cameras and offer a real-time view without any delay.
Electronic Viewfinder (EVF): Found in mirrorless cameras, EVFs display a digital image of what the camera’s sensor sees. This allows for features like live histograms, focus peaking, and real-time exposure adjustments, offering a more versatile viewing experience.
Both types have their strengths, and the choice largely depends on personal preference and shooting style.
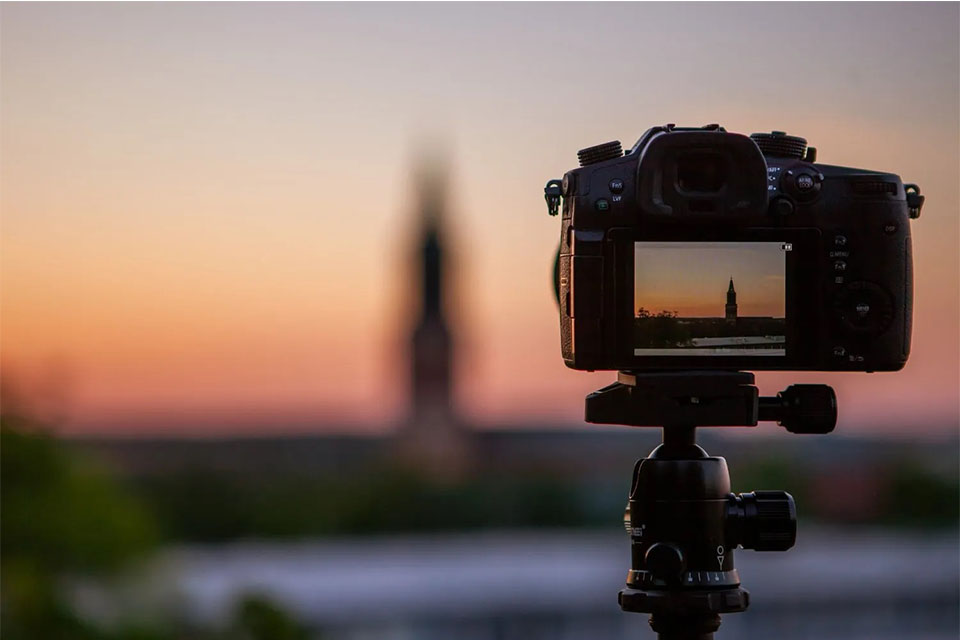

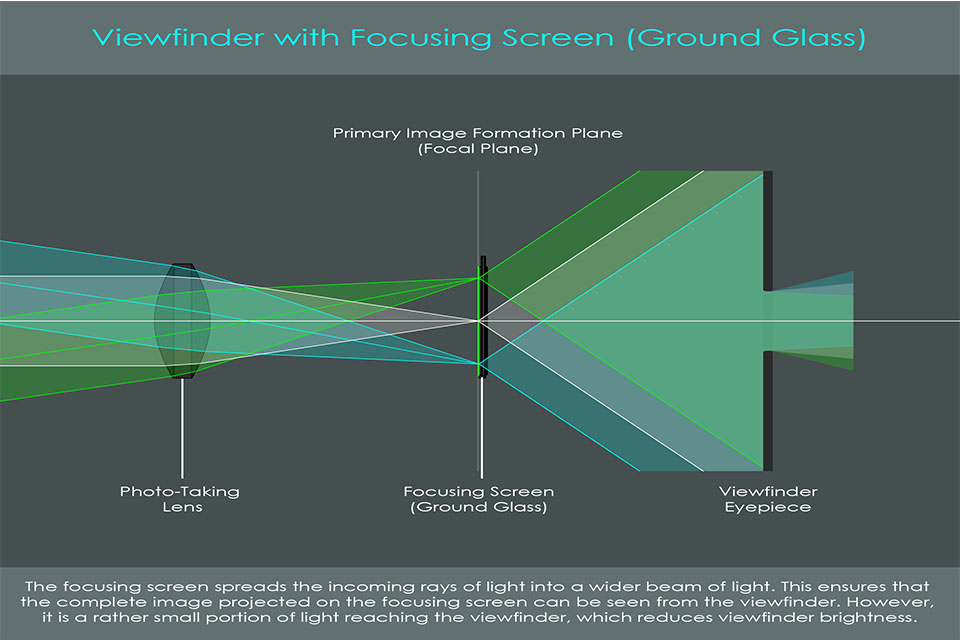
An optical viewfinder operates using a series of mirrors and prisms to reflect light from the lens to your eye. When you look through the viewfinder, you see the scene as it is, without any digital processing. This means that what you see is precisely what will be captured, provided your camera settings are correct.
One of the key benefits of an optical viewfinder is its immediacy. Since there is no electronic delay, you can react quickly to fast-moving subjects. Additionally, optical viewfinders typically perform well in low-light conditions, providing a bright and clear image, making them a preferred choice for many photographers.
An electronic viewfinder utilizes a small LCD or OLED screen to display a digital representation of the scene captured by the camera’s sensor. This allows for a more interactive experience, as you can see how changes in settings affect exposure and color in real-time.
EVFs offer advantages such as the ability to display overlays, including gridlines and exposure levels, which can assist in composing your shot. Additionally, they allow for better visibility in low-light scenarios, as the display can be adjusted for brightness. However, some photographers find that EVFs can have a slight lag, which may affect fast-paced shooting.
Using a viewfinder effectively involves a few key techniques. First, ensure that your eye is properly aligned with the viewfinder. This alignment helps you see the full frame without any obstruction, allowing for better composition.
Next, practice utilizing the camera settings visible through the viewfinder. Many cameras provide essential information such as shutter speed, aperture, and ISO settings in the viewfinder, helping you make quick adjustments as needed. Familiarizing yourself with these settings can significantly enhance your shooting experience.
Camera settings play a crucial role in how you utilize the viewfinder. For instance, adjusting the aperture impacts the depth of field, which can be seen in the viewfinder. A wider aperture creates a blurred background, helping to isolate your subject, while a smaller aperture increases the depth of field, bringing more elements into focus.
Moreover, understanding how ISO affects exposure is vital. In low-light conditions, increasing the ISO can brighten your image, but it may also introduce noise. This balance is something you can monitor through the viewfinder, allowing for more informed shooting decisions.
Many photographers prefer using viewfinders for several reasons. One significant factor is the enhanced stability they provide. By anchoring your eye to the viewfinder, you create a more stable shooting platform, which can reduce camera shake and lead to sharper images.
Additionally, viewfinders allow for a more immersive shooting experience. When you look through a viewfinder, you are fully engaged in the scene, which can foster a deeper connection to your subject. This engagement often translates into more thoughtful compositions and creative choices.
Changing camera settings while using the viewfinder is typically straightforward. Most modern cameras allow you to access settings through the viewfinder display. You can adjust ISO, shutter speed, and aperture without taking your eye away from the viewfinder, making the process efficient.
Familiarizing yourself with your camera’s layout and controls will enhance your ability to make quick adjustments. Many photographers recommend practicing these changes until they become second nature, allowing you to focus on capturing the perfect shot rather than fiddling with settings.
As you explore the world of photography, keep these key points about viewfinders in mind:
Viewfinders enhance framing and composition, providing a direct view of your subject.
They can improve stability, especially in challenging lighting conditions.
Understanding the differences between optical and electronic viewfinders can help you choose the right camera.
Familiarizing yourself with camera settings through the viewfinder can streamline your shooting process.

What is a Viewfinder? A tool for framing shots accurately.
Why Use It? Better visibility in bright light and improved stability.
Types of Viewfinders: Optical vs. Electronic.
Using Effectively: Align your eye and utilize settings.
Camera Settings Matter: Adjust aperture and ISO for better results.
Photographer Preference: Stability and engagement are key.
Adjusting Settings: Quick access through the viewfinder enhances efficiency.
By understanding the importance of viewfinders and how to use them effectively, you can significantly enhance your photography skills and create more compelling images. Happy shooting!
Contact: Ashley Wu
Phone: +86 17773983073
E-mail: [email protected]
Add: 708 Room A Buiding Huafeng International Robot Industrial Park Xixiang Bao'an