This article dives into the world of Head-Mounted Displays (HMDs), commonly known as VR headsets, explaining their function, technology, and diverse applications. From gaming to professional simulations, HMDs are revolutionizing how we interact with digital content. If you want to stay on the cutting edge of virtual reality technology, this comprehensive guide is for you. It will give you the knowledge you need to select right vr headset.
A VR headset, more technically known as a Head-Mounted Display (HMD), is a device worn on the head that provides immersive visual and auditory virtual reality experiences. The core function of an HMD is to create an artificial environment, a virtual environment that replaces the user’s real-world surroundings with computer-generated visuals and sounds. This is achieved through stereoscopic displays, where separate images are presented to each eye, creating a sense of depth and three-dimensionality.
The headset typically includes a display screen, lenses, and sensors. The display screen presents the visual content, while the lenses focus the image for each eye, allowing the user to perceive depth. Sensors within the headset track the user’s head movements, allowing the virtual environment to respond dynamically to changes in the user's viewpoint. This head tracking is crucial for maintaining the illusion of presence within the vr environment. Some vr headsets also incorporate headphones for immersive audio, further enhancing the virtual reality experience. Used in virtual reality gaming, the VR headset is typically used in conjunction with controller which allow user to interact with the VR environment.

The display is a core component of any vr headset and is responsible for creating the visual information that immerses the user in the virtual reality world. Several technologies are used in VR headset displays, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Common display types include LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) and OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) panels. LCD panels are known for their brightness and clarity, while OLED panels offer better contrast ratios and deeper blacks. The choice of display technology affects visual fidelity and the overall vr experience.
The lens is the crucial component that focuses the light from the display screen onto the user’s eyes. They are specifically designed to create a comfortable viewing experience at close range. The design and quality of the lenses can significantly impact the sharpness, clarity, and field of view of the vr experience. Lens aberrations, such as distortion or chromatic aberration, can detract from the immersion and cause eye strain. The quality of the lens affects clarity. Modern vr headsets often employ advanced lens designs to minimize these distortions and maximize visual fidelity. The visual information is delivered by these components.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Display Panel | Presents the visual content of the virtual environment. |
| Lenses | Focus light from the panel onto the user's eyes, creating a clear image. |
| Head Tracking Sensors | Track the user's head movements, allowing the virtual environment to respond. |
| Audio System | Provides immersive sound to complement the visual vr environment. |
Head tracking is a cornerstone of virtual reality technology, enabling the user to move their head and have the virtual environment respond accordingly in real time. The primary goal of head tracking is to maintain the illusion of presence, where the user feels like they are genuinely inside the virtual world. Without accurate head tracking, the virtual environment would feel static and disconnected, diminishing the immersion.
Head tracking technology relies on a variety of sensors integrated into the vr headset to monitor the user's head movements. These sensors typically include accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers. Accelerometers measure linear acceleration, gyroscopes measure angular velocity, and magnetometers measure the Earth's magnetic field. By combining data from these sensors, the vr headset can accurately track the user's head orientation and position. Sophisticated algorithms process the sensor data to filter out noise and compensate for drift, ensuring precise and responsive head tracking. Head and present visuals correctly.
VR headsets, or HMDs, come in several different types, each offering a unique level of immersion and functionality. One way to categorize vr headsets is by their processing power and connectivity:
Tethered VR Headsets: These vr headsets, such as the Oculus Rift and HTC Vive, require a physical connection to a powerful PC or gaming console. They offer high-fidelity graphics and advanced features due to the computing power of the attached device.
Standalone VR Headsets: These vr headsets, such as the Oculus Quest 2, have all the necessary processing power built-in, allowing for wireless vr experiences. Standalone vr headsets offer convenience and portability.
Mobile VR Headsets: These vr headsets use a smartphone as the display and processing unit. Mobile VR headsets, like the Samsung Gear VR, were an early entry into the vr market but have largely been superseded by standalone options.
Another classification can be based on the level of tracking and interaction they offer. Some vr headsets provide basic rotational tracking, while others support positional tracking, allowing users to move around in the virtual environment. Advanced vr headsets may also incorporate hand tracking or eye tracking for more natural and intuitive interactions.

Display resolution and refresh rate are critical specifications that determine the visual quality and smoothness of the vr experience in vr headsets. Resolution refers to the number of pixels per eye in the display, typically expressed as width x height. Higher resolution vr headsets offer sharper and more detailed visuals, reducing the screen-door effect, where the individual pixels become visible. Pixel density is closely related to resolution and refers to the number of pixels per inch (PPI) on the display. A higher pixel density results in a clearer and more immersive visual experience.
Refresh rate refers to the number of times per second that the display updates its image, measured in hertz (Hz). A higher refresh rate reduces motion blur and ghosting, resulting in a smoother and more comfortable vr experience. The refresh rate is closely related to latency. Common refresh rates for vr headsets range from 75 Hz to 120 Hz or higher. A 120 hz refresh rate minimizes motion sickness and enhances the sense of presence.
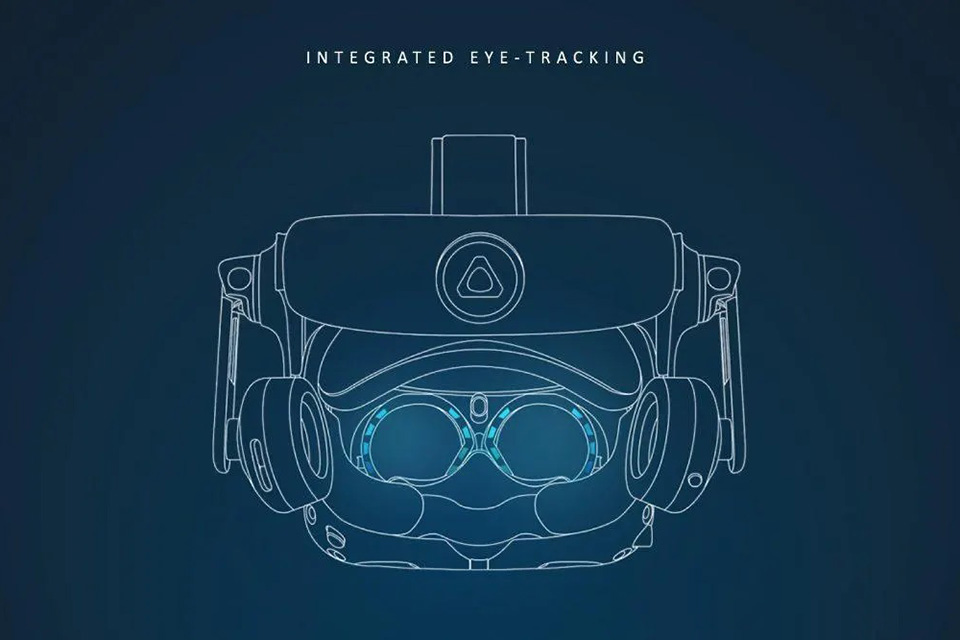
Eye tracking technology is gaining traction as a new category of feature in vr headsets, promising to revolutionize how users interact with virtual environments. Eye tracking involves using sensors to monitor the user’s gaze direction and eye movements. This data can be used for a variety of purposes, including:
Foveated Rendering: This technology renders the area of the vr environment that the user is directly looking at in high detail, while reducing the resolution of peripheral areas. This can significantly reduce the computational load on the graphics processing unit (GPU), allowing for higher overall visual fidelity.
User Interface (UI) Navigation: Eye tracking allows users to navigate menus and interact with virtual objects simply by looking at them. This can provide a more natural and intuitive user interface compared to traditional controller-based input.
Social Interaction: In social vr environments, eye tracking can be used to convey emotions and intentions through eye contact and gaze direction. This can make virtual interactions feel more realistic and engaging.
While eye tracking is still an emerging technology in vr, its potential to enhance immersion and interaction is immense. As eye tracking technology matures and becomes more affordable, it is likely to become a standard feature in high-end vr headsets.
Latency, the delay between a user's action and the corresponding reaction in the virtual environment, is a critical factor that affects the vr experience. High latency can lead to motion sickness and a reduced sense of presence. Several factors contribute to latency in vr headsets, including:
Display Refresh Rate: Lower refresh rates result in longer delays between frames, increasing overall latency.
Sensor Processing Time: The time it takes for the vr headset's sensors to track head movements and update the virtual environment.
Graphics Rendering Time: The time it takes for the GPU to render each frame of the virtual environment.
Communication Delays: Delays in communication between the vr headset, the PC or console, and any input devices.
Minimizing latency requires optimizing each of these factors. High-performance GPUs, fast display panels, and efficient sensor processing algorithms are essential for achieving low latency.
HMDs are not limited to virtual reality; they also play a crucial role in augmented reality (AR) and extended reality (XR) technologies. While vr headsets create fully immersive virtual environments, AR headsets overlay digital information onto the real world. XR is an umbrella term that encompasses both vr and AR, along with other emerging technologies that blend the physical and digital worlds. HoloLens is a notable example.
AR headsets, like the Microsoft HoloLens, use optical see-through or video see-through technology to display digital information in the user's field of view. These vr headsets can be used for a wide range of applications, including training, education, and remote collaboration. XR devices seek to integrate the best aspects of vr and AR, creating seamless transitions between the real and virtual worlds. As technology advances, the lines between vr, AR, and XR are becoming increasingly blurred.
While traditional vr headsets use display screens and lenses to project images onto the user's eyes, several advanced HMD technologies are being developed to enhance visual fidelity and immersion. One such technology is retinal projection, which involves projecting images directly onto the retina using lasers or other light sources. Retinal projection offers several potential advantages, including:
High Resolution: Retinal projection can achieve extremely high resolutions, exceeding the capabilities of traditional display screens.
Wide Field of View: Retinal projection can create a wider field of view, enhancing the sense of immersion.
Improved Clarity: By projecting images directly onto the retina, retinal projection can eliminate the need for lenses, reducing distortions and improving clarity.
In addition to retinal projection, other advanced HMD technologies include light field displays, which create a more realistic depth perception, and holographic displays, which project three-dimensional images into space. These emerging technologies hold the promise of creating even more immersive and realistic vr experiences.
The best vr headset for you will depend on your specific needs and budget. Here are a few of the top vr headsets currently available:
Valve Index: Known for its high-fidelity vr experience and precise head tracking, the Valve Index is a top choice for PC VR enthusiasts. It features high refresh rate and high-resolution displays.
HTC Vive Pro 2: Designed for professional users and vr enthusiasts, the HTC Vive Pro 2 offers exceptional visual fidelity and a wide field of view. HTC vive integrate with Steam VR platform.
Oculus Quest 2 (Meta Quest 2): A standalone vr headset that offers a compelling balance of performance, affordability, and convenience, oculus quest has been a popular choice for both new and experienced vr users.
HP Reverb G2: Known for its high-resolution displays, the HP Reverb G2 offers a visually stunning vr experience at a competitive price.
PlayStation VR2: Designed for PlayStation 5, the PlayStation VR2 offers a high-quality vr experience with advanced features like eye tracking and haptic feedback.
When choosing a vr headset, consider factors such as resolution, refresh rate, head tracking accuracy, comfort, and the availability of content. The best way to find the right vr headset for you is to try out several different models and see which one provides the most immersive and enjoyable vr experience.
Definition: A VR headset (HMD) creates an immersive virtual reality experience by displaying stereoscopic images and tracking head movements.
Core Components: The main parts of an HMD are the display panel, lenses, head tracking sensors, and often, an audio system.
Head Tracking Importance: Accurate head tracking is crucial for a realistic and immersive virtual reality experience.
Types of VR Headsets: VR headsets can be tethered to a PC or console, standalone, or mobile (using a smartphone).
Resolution and Refresh Rate: Higher resolution and refresh rates improve visual quality and reduce motion blur.
Eye Tracking Potential: Eye tracking can enhance user interaction, enable foveated rendering, and improve social vr experiences.
Latency Matters: Low latency is essential to prevent motion sickness and maintain a sense of presence.
VR Beyond VR: HMDs are also used in augmented reality (AR) and extended reality (XR) applications.
Advanced Technologies: Retinal projection and other emerging display technologies could revolutionize vr visuals.
Choosing the Right VR Headset: Consider your needs, budget, and desired level of immersion when selecting a vr headset.
Contact: Ashley Wu
Phone: +86 17773983073
E-mail: [email protected]
Add: 708 Room A Buiding Huafeng International Robot Industrial Park Xixiang Bao'an