AR (augmented reality) and VR (virtual reality) are two different virtual reality technologies, which provide different experiences and application scenarios.


Definition: AR is a technology that integrates virtual elements with the real environment by superimposing digital information on the real world to provide an enhanced and rich user experience.
Experience: Users observe the real world through AR devices (such as AR glasses, smartphones or tablets), and at the same time see digital information superimposed on objects, which can include text, images, videos, etc.
Application scenarios: AR is widely used in real-time navigation, virtual fitting, education and training, repair and maintenance, healthcare and other fields. In real-time navigation, users can see navigation instructions displayed directly on the road through AR; in virtual fitting, users can use AR to see themselves wearing different clothes on the screen.
Definition: VR is a technology that completely replaces reality with a virtual environment, immersing users in a virtual scene.
Experience: Users completely detach from the real world and enter a virtual environment by wearing a VR headset. This environment is usually presented through computer-generated three-dimensional graphics or 360-degree video.
Application scenarios: VR has a wide range of applications in games, virtual tourism, simulation training, psychotherapy and other fields. In virtual tourism, users can experience places far away from home through VR; in simulation training, VR can provide a real-feeling training environment, such as a flight simulator.
Immersion level: VR provides complete immersion, and users cannot perceive the real world. AR adds virtual elements to reality, and users can still perceive the surrounding environment.
Equipment: VR usually requires a dedicated headset device, while AR can be achieved through smartphones, tablets or AR glasses.
Application areas: AR focuses more on interaction with the real world and is suitable for scenarios where digital information needs to be superimposed in the real environment; VR is more suitable for applications that require users to be completely immersed in a virtual environment.
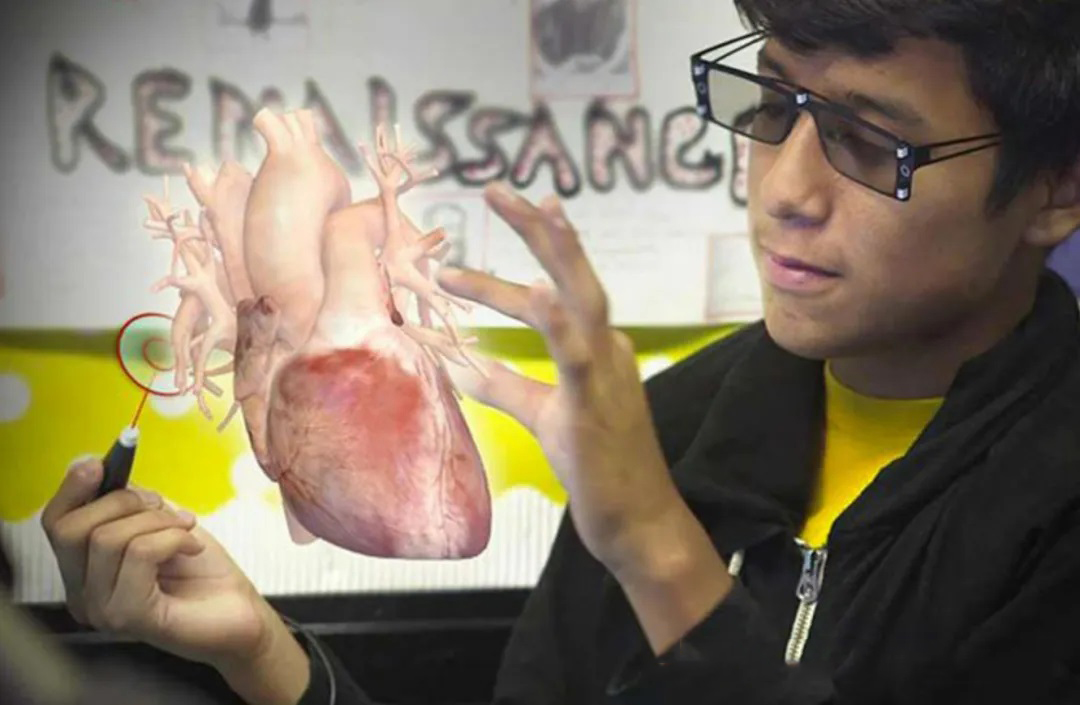
Definition: Mixed reality is a technology between augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), which integrates the real world and the virtual world, allowing physical and digital objects to coexist and interact in the same space.
Experience: Users can see and perceive the real world, and can also interact with virtual elements. Compared with AR, MR pays more attention to integrating virtual and real elements more closely, making the interaction between the two more natural.
Application scenarios: MR's application scenarios include virtual meetings, virtual training, medical surgery simulation, etc. In virtual meetings, participants can participate in meetings together in virtual space and share virtual real-time content; in medical surgery simulation, doctors can use virtual elements to simulate surgery in addition to real patients.
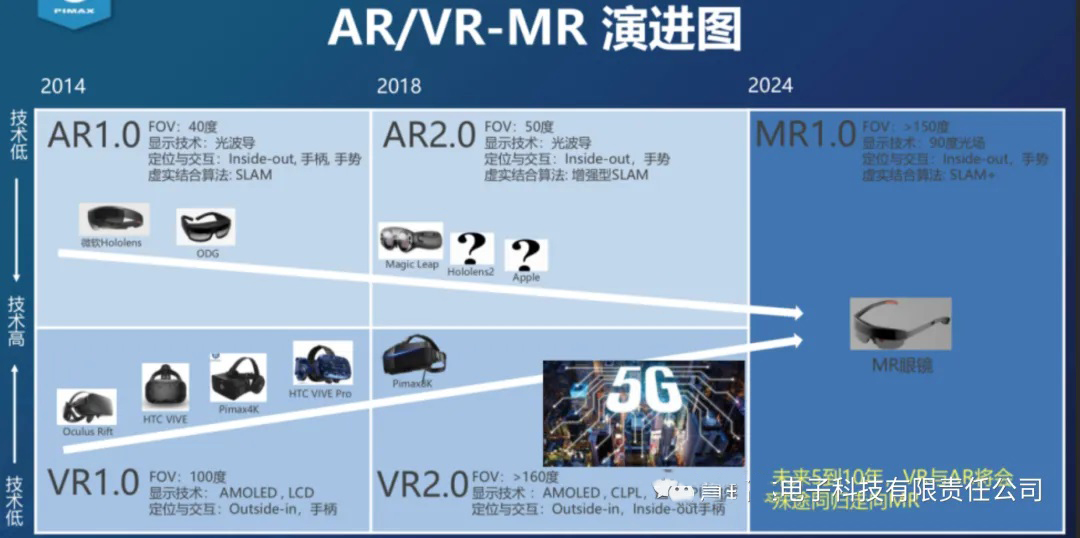
Integrated development: AR, VR, and MR may be more integrated in the future to form a more comprehensive and integrated virtual reality experience. Under this trend, users can experience the functions of AR, VR, and MR on the same device.
Application expansion: With the continuous development of technology, AR, VR, and MR will be applied in more fields, including education, medical care, industrial manufacturing, artistic creation, etc. Technological advances will drive deeper applications of these technologies in various industries.
Hardware innovation: With the continuous innovation of hardware technology, AR, VR, and MR devices will become lighter, more comfortable, and more intelligent. This will enhance user experience and promote the wider popularization of virtual reality technology.
Education: AR, VR, and MR will be more widely used in the field of education. Virtual reality can provide immersive learning experiences, such as virtual field trips, restoration of historical scenes, anatomical learning, etc. This helps to improve students' interest in learning and the depth of their understanding.
Healthcare: In the medical field, these technologies can be used for surgical simulation, patient treatment, medical training, etc. Virtual reality technology can provide a more realistic simulation environment to help doctors improve their skills.
Corporate training: In the field of corporate training, AR, VR, and MR can provide a simulated working environment, train employees to cope with different situations, reduce training costs, and improve training effectiveness.
Social interaction: Virtual reality technology will play a greater role in the field of social entertainment. People can conduct social activities such as virtual meetings, virtual gatherings, and multiplayer games through virtual reality spaces.
Art and cultural experience: Virtual reality technology provides artists and cultural and creative industries with new ways of expression. Users can experience artworks, participate in virtual exhibitions, or experience cultural activities such as music and drama in a virtual reality environment through AR.
Smart city: AR, VR, and MR are expected to be combined with the development of smart cities to provide smarter and more convenient urban services. For example, AR navigation can provide real-time information in cities, and VR can simulate urban planning schemes.
Wearable devices: As wearable device technology advances, AR glasses and VR headsets will become lighter and more comfortable, providing a better virtual reality experience. This will prompt more users to accept these technologies.
Technology Convergence: In the future, AR, VR, and MR may be more integrated to create a more comprehensive virtual and augmented reality experience. This may include all-in-one devices that support multiple virtual experiences at the same time.

Contact: Ashley Wu
Phone: +86 17773983073
E-mail: [email protected]
Add: 708 Room A Buiding Huafeng International Robot Industrial Park Xixiang Bao'an